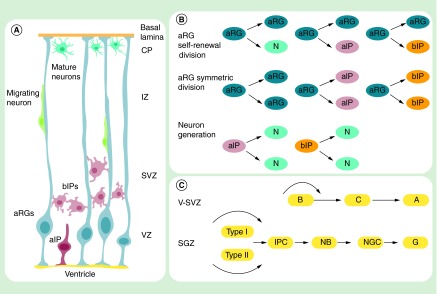
Figure 1. . Neurogenesis in the embryonic and adult stage.
(A) aRGs can produce aIPs and bIPs, which can be divided symmetrically to generate neurons. Newborn neurons migrate along the basal process of aRGs to form the cortical plate. (B) aRGs can undergo asymmetric self-renewing division to generate one daughter aRG and one more differentiated cell, such as a(n) neuron, aIP and bIP. aIP and bIP undergo one round of symmetric division to generate neurons. aRGs can also proliferate and generate aIP and bIP by symmetric divisions. (C) Cell lineage in the V-SVZ and SGZ during adult neurogenesis.
A: Type A cell; aIP: Apical intermediate progenitor; aRG: Apical radial glial cell; B: Type B cell; bIP: Basal intermediate progenitor; C: Type C cell; CP: Cortical plate; GC: Granular cell; IPC: Intermediate progenitor cell; IZ: Intermediate zone; N: Neuron; NB: Neuroblast; NGC: New granular cell; SGZ: Subgranular zone; SVZ: Subventricular zone; V-SVZ: Ventricular-subventricular zone; VZ: Ventricular zone.