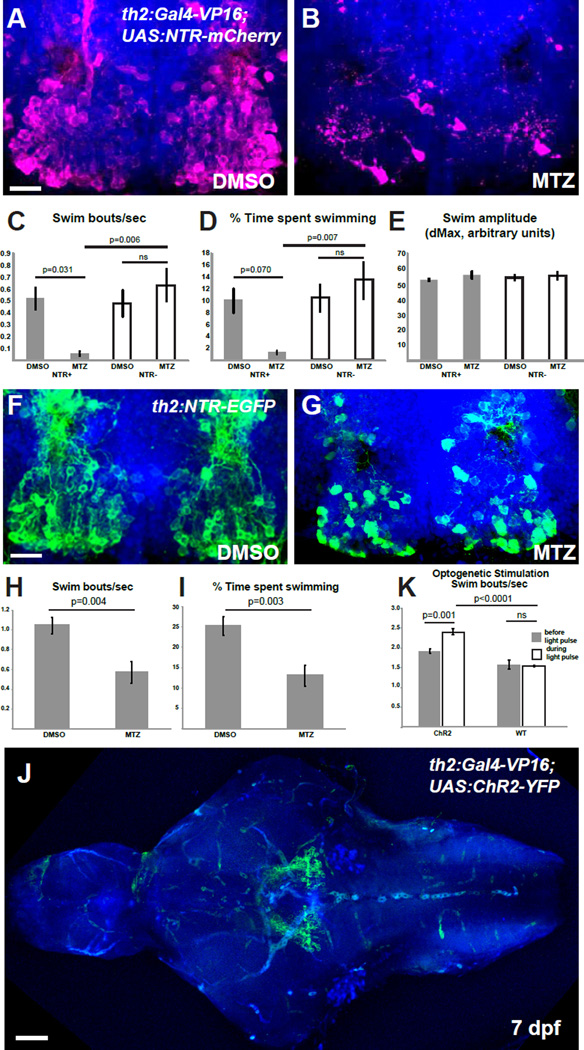
Figure 3. th2+ cells modulate the initiation of swimming behavior.
(A–B) Representative brains of 8 dpf th2:Gal4-VP16; UAS:NTR-mCherry larvae treated with 0.5% DMSO (A) or 5mM MTZ (B) from 5–7 dpf. (C–E) Effects of ablation on behavior in 8 dpf larvae as measured by swimming frequency (C) time spent swimming (D), and swim amplitude (E) Error bars=SEM, n=6 larvae for each condition except NTR+ fish treated with MTZ, wherein n=5 due to exclusion of an outlier (p<0.01, Grubbs’ test). Two-way ANOVA indicates a significant interaction between genotype and treatment for swim initiations (p=0.009 for swim frequency; p=0.020 for swim time), but not for swim amplitude. Adjusted p values shown for pairwise comparisons are based on Bonferroni Multiple Comparison test. (F–G) Representative brains from 8 dpf th2:NTR-EGFP larvae treated with 0.5% DMSO (F) or 5mM MTZ (G) from 5–7 dpf. (G–H) Effects of ablation on swimming behavior in 8 dpf larvae as measured by swimming frequency (H) and time spent swimming (I). Error bars=SEM, n=8 individual larvae for each condition. p values based on Student t-test. See Figure S1 for whole-animal images of NTR transgene expression, representative plots of swimming behavior, and control ablations of radial glia. (J) Representative brain of th2:Gal4: UAS:ChR2-YFP larva, showing that most axons appear to terminate nearby in the posterior tuberculum. (K) Average swim bouts/sec before and during blue light pulse for individual larvae. Error bars=SEM, n=4 (wild-type), n=5 (ChR2). Two-way ANOVA demonstrates significant interaction between genotype and light exposure (p=0.0025). Adjusted p values shown for pairwise comparisons are based on Bonferroni Multiple Comparison test. Images in (A–B,F–G,J) are ventral maximum intensity confocal Z-projections of the brain. Scale bar = 10µM. See Figure S1 for whole-animal images of ChR2 expression, and examples of neuronal activity and swimming behavior after stimulation.