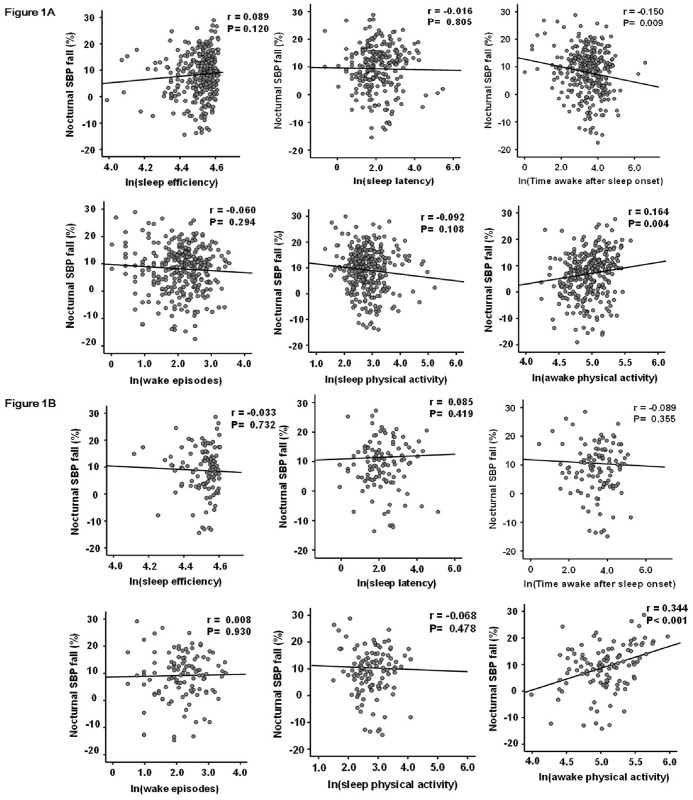
Fig 1. Pearson's correlation coefficients among objective parameters for sleep disturbances, ambulatory physical activity, and nocturnal SBP fall in all subjects and subgroup patients without anti-hypertensive medications.
The parameters of objective sleep disturbances and ambulatory physical activity were natural logarithm-transformed (ln) to achieve a normal distribution. In all subjects, time awake after sleep onset (r = -0.150, P = 0.009) and awake physical activity (r = 0.164, P = 0.004) were significantly associated with nocturnal SBP fall (Fig 1A). In subgroup patients without anti-hypertensive medications, only awake physical activity (r = 0.344, P < 0.001) were significantly associated with nocturnal SBP fall (Fig 1B). SBP denotes systolic blood pressure. r: Pearson's correlation coefficient.