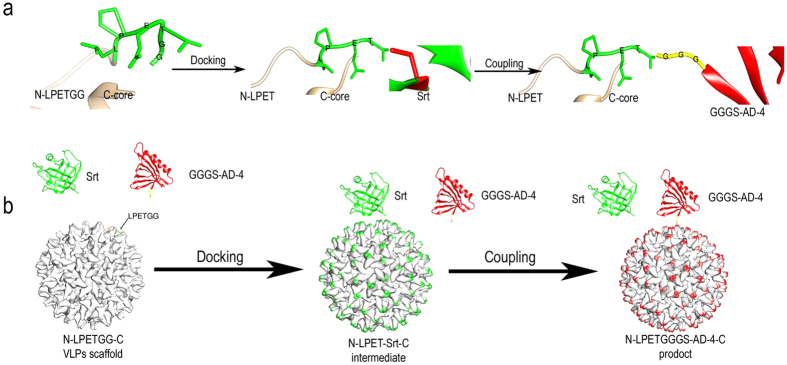
Figure 1. Schematic depiction of chemoenzymatic site-specific coupling of GGGS-AD-4 to N-LPETGG-C VLPs.
(a) Site-specific focus view of the 3D structures at the LPETGG site during coupling process by UCSF Chimera. The LPETG motif on the N-LPETGG-C VLP surface is recognized by sorase A-4, and the T- and G-bond is cleaved by enzyme. The sortase A-4 is acylated at cysteine 184 with threonine at the “docking” step. The intermediate is then resolved by GGGS-AD-4 nucleophilic attack. GGG-based antigens are thus coupled to the VLP scaffold. (b) The dynamic process of reaction is illustrated. The models of sortase A-4 (Srt, green), GGGS-AD-4 (red), and N-LPETGG-C VLPs (white) were generated by MODELLER and viewed with UCSF Chimera. At the docking step, sortase A-4 forms an intermediate with the VLP scaffold, and the spikes of the VLPs are decorated by sortase A-4 (green). GGGS-AD-4 then couples to the VLP, and the spikes are modified by GGGS-AD-4 (red).