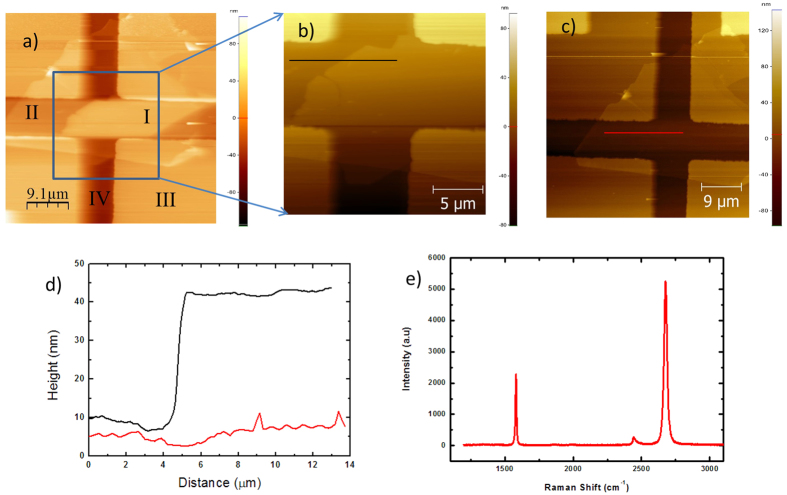
Figure 3.
(a) AFM topographic image of the graphene on hBN sample in ambient conditions with scan size 45 μm. (b) The graphene area on top of hBN was rescanned in air. The shape of graphene was clear with increased thickness as absorbing gases or moisture from surrounding. (c) AFM image of the graphene on hBN measured immediately after exposing air from in-vacuum at 1 × 10−5 Torr with scan size 40 μm. In this image, single-layer graphene was invisible as the condensed moisture was removed in vacuum. (d) The height profiles along lines in (b,c) are shown, respectively. The thickness of the graphene layer including condensed moisture was ~30 nm. (e) Raman spectroscopy data were measured to confirm it as a single-layer graphene.