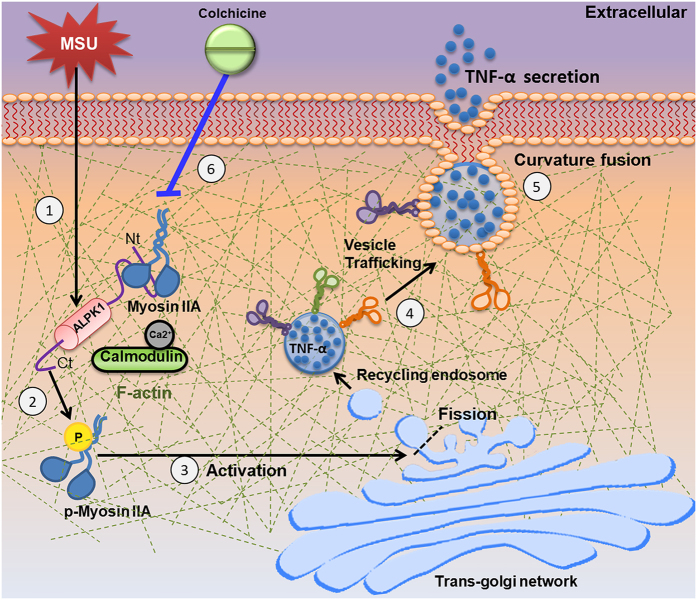
Figure 7. Possible role of ALPK1 in gouty inflammation.
(1) MSU crystals stimulate ALPK1 gene overexpression in the monocyte. (2) One of α-kinase’s functions is bind with myosin IIA via N-terminal (Nt) while C-terminal (Ct) phosphorylates the motor protein in presence of ATP. (3) Activated myosin IIA at the Golgi membrane. (4) Transport of Golgi-derived TNF-α vesicles. (5) Transport towards plasma membrane and contribute to secretion of TNF-α. (6) ALPK1 is unaffected by colchicine, so MSU persists in stimulating ALPK1 expression. However, colchicine (blue line) disrupts microtubule formation, which myosin motor proteins act upon, thus less myosin is recruited, resulting in less vesicular delivery of TNF-α. An aberrant ALPK1 or knockdown may decrease phosphorylation of myosin IIA and lower TNF-α secretion.