Figure 2.
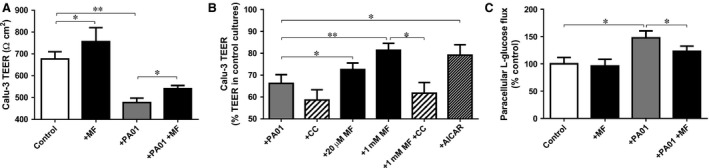
Metformin prevents the effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection on transepithelial resistance and paracellular glucose flux across the airway epithelium. (A) The effect of metformin pre‐treatment (MF; 1 mM, 18 hrs prior to addition of P. aeruginosa) on Calu‐3 monolayer transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER; Ω/cm2), in the presence and absence of P. aeruginosa (7 hr co‐culture), under normoglycaemic conditions (5 mM basolateral glucose), n = 5, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (B) The effect of metformin (MF; 20 μM or 1 mM, 18 hr pre‐treatment), AICAR (0.5 mM, 18 hr pre‐treatment) and AMPK inhibitor compound C (CC; 80 μM pre‐treatment for 1 hr prior to addition of metformin) on Calu‐3 monolayer TEER (percentage compared with mean TEER in uninfected control Calu‐3 cultures) in co‐culture with P. aeruginosa (7‐hr co‐culture), under normoglycaemic conditions (5 mM basolateral glucose), n = 6, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) Paracellular glucose flux across uninfected and P. aeruginosa infected Calu‐3 monolayers, with and without pre‐treatment with 1 mM metformin. Paracellular flux measured by adding radiolabelled L‐glucose to the basolateral surface and monitoring its appearance at the apical surface, n = 4, *P < 0.05.
