Fig. 6.
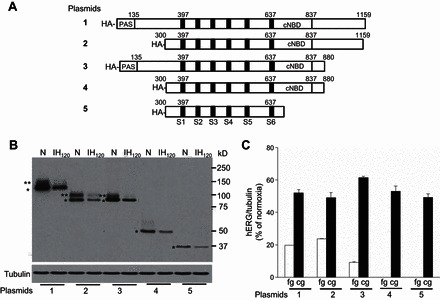
Contribution of NH2 terminus and COOH terminus of hERG in IH-induced hERG degradation by calpains. A: schematic diagram showing the full-length wild-type (WT; 1); NH2 terminus (2); COOH terminus (3); and both NH2- and COOH-terminal (4 and 5) deleted plasmids with HA-tag. B: representative immunoblot showing hERG protein expression in SH-SY5Y cells with forced expression of WT hERG (1) and NH2 (2) and COOH (3) terminus and NH2- and COOH (4 and 5)-terminal truncated constructs exposed to either normoxia or IH120. The recombinant hERG proteins were detected with anti-HA antibody (Acris Antibodies; AP23352PU-N). Tubulin protein expression was used as a loading control. **Full glycosylated (fg) form of hERG protein. *Core glycosylated (cg) form of hERG protein. C: densitometric analysis (means ± SE from 3 individual experiments) of fg and cg forms of hERG protein normalized to tubulin and expressed as percentage of normoxia.
