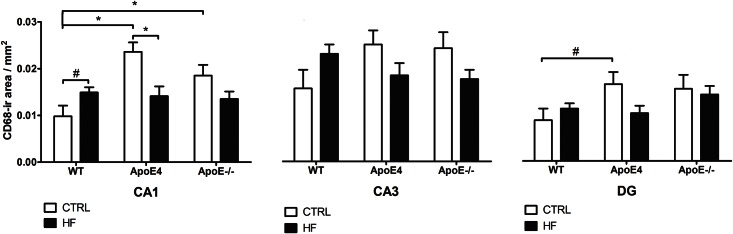
Fig 4. CD68 immunoreactivity.
In the CA1, we observed a genotype × diet interaction (p = 0.001), there was a trend for increased inflammation in WT after HF supplementation (p = 0.052). Inflammation in ApoE4 mice significantly decreased after HF supplementation (p = 0.009). ApoE4 mice on CTRL demonstrated increased inflammation compared to WT mice on CTRL (p = 0.001). ApoE-/- compared to WT mice showed a genotype × diet interaction (p = 0.010). ApoE-/- on CTRL demonstrated increased inflammation when compared to WT mice on CTRL (p = 0.032). In the CA3, a genotype × diet interaction was observed (p = 0.024) but no significant effect on inflammation caused by genotype or diet when comparing ApoE4 to WT mice. Furthermore, ApoE-/- compared to WT mice showed a genotype × diet interaction (p = 0.023). No significant effects on inflammation caused by genotype or diet were found though. In the DG, we observed a genotype × diet interaction (p = 0.047) when comparing ApoE4 to WT mice. There was a trend for increased inflammation in ApoE4 mice on CTRL diet compared to WT mice on CTRL (p = 0.063). In addition, ApoE-/- displayed increased inflammation when compared to WT mice (p = 0.029). Values represent mean±SEM; WT CTRL n = 5, WT HF n = 7, ApoE4 CTRL n = 7, ApoE4 HF n = 5, ApoE-/- CTRL n = 4, ApoE-/- HF n = 6. *p≤0.05, #0.05<p<0.07. ApoE = apolipoprotein E; CA1 = cornu ammonis 1; CA3 = cornu ammonis 3; CD68 = cluster of differentiation 68; CTRL = control; DG = dentate gyrus; HF = high-fat; WT = wild-type.