Fig. 3.
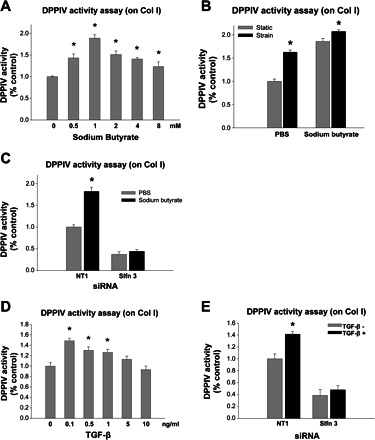
Schlafen-3 reduction by siRNA also inhibited the stimulation of DPPIV activity by 24-h treatment with sodium butyrate (1 mM) or transforming growth factor (TGF)-β (0.1 ng/ml). A: sodium butyrate, a differentiating agent, stimulated DPPIV activity in IEC-6 cells plated on collagen I (Col I) (n = 4, *P < 0.01). B: DPPIV activity was increased by strain and sodium butyrate (1 mM), indicating that sodium butyrate induces differentiation by a different mechanism from strain (n = 3; *P < 0.05). C: cells plated on collagen I and transiently transfected with siRNA targeted to Schlafen 3 (Slfn 3) or nontargeting NT1 sequences were treated with sodium butyrate (1 mM) before lysis and assay for DPPIV-specific activity. DPPIV activity was increased by sodium butyrate (1 mM) to 1.82 ± 0.09 in NT1-treated cells, but this effect was completely blocked by transfection with Schlafen 3 siRNA (n = 5, *P < 0.05). D: TGF-β, another well-characterized differentiating agent, stimulated DPPIV activity in IEC-6 cells plated on collagen I (n = 4, *P < 0.01). E: in IEC-6 cells plated on collagen I, addition of TGF-β stimulated DPPIV to 1.41 ± 0.04, and this effect was similarly prevented by reducing Schlafen 3 with siRNA (n = 3; *P < 0.05).
