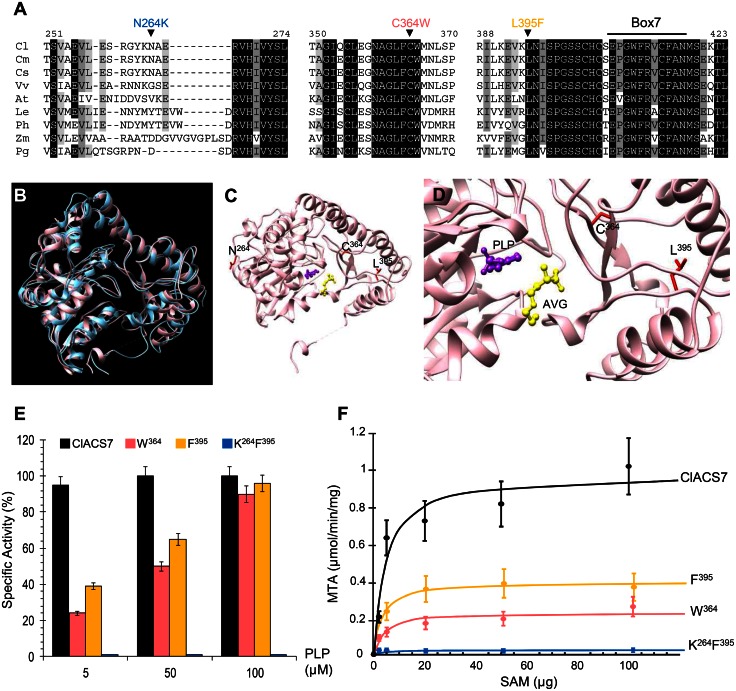
Fig 4. Molecular characterization of ClACS7 alleles.
(A) Amino acid alignments of ClACS7 isoform with homologous proteins from Cm (Cucumis melo), Cs (Cucumis sativus), Vv (Vitis vinifera), At (Arabidopsis thaliana), Le (Lycopersicum esculentum), Ph (Petunia hybrida), Zm (Zea mays) and Pg (Picea glauca). Numbers above the alignment indicate the amino acid positions along the ClACS7 protein. Box 7 indicates a conserved domain in ACS proteins. N264K, C364W and L395F amino acid polymorphisms are shown above the alignment. (B-D) Model of the three-dimensional structure of ClACS7. (B) Superposition of the tomato ACS 3D crystal structure (1IAY.pdb) indicated in blue and the 3D model of ClACS7 indicated in pink. The three-dimensional structure were generated using the Geno3D server (http://geno3d-pbil.ibcp.fr) and the visualization was carried out using the Chimera server (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera). (C and D) Zoom in on the active site of ClACS7. The residues that are polymorphic in the different ClACS7 isoforms are depicted in red. The cofactor PLP is indicated by purple ball and stick. The competitive inhibitor AVG (aminoethoxyvinylglycine) is indicated by yellow ball and stick. (E and F) Biochemical characterization of ClACS7, W364, F395 and K264F395 enzyme isoforms. (E) Enzymatic activity of ClACS7 (black bars), W364 (pink bars), F395 (orange bars) and K264F395 (blue bars) protein forms. Specific activities were measured on dialyzed enzymes in the presence of 60 μM SAM and various PLP concentrations. (F) Initial velocity of the ClACS7 isoforms measured at 50 mM of PLP. Experimental data were fit into a line following Michaelis-Menten equation.