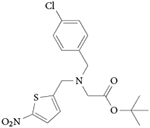
GSK4112
(also known
as SR6452) |
|
Agonist Targets REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ REV-ERBα EC50 = 0.4 μM (measured by FRET assay) REV-ERBα EC50 = 2.3 μM (measured by Bmal1 luciferase reporter assay) Suppresses expression of REV-ERB target genes in cells Induces adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells Lowers glucose output in primary mouse hepatocytes Resets circadian oscillation of REV-ERB target genes in cells Has a limited in vivo exposure, which limits its use as a chemical tool in vivo
|
71,101,
102
|
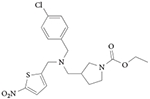
| SR9009 |
|
Agonist REV-ERBα EC50 = 0.67 μM (measured by Gal4 reporter assay) REV-ERBα EC50 = 0.71 μM (measured by full-length Bmal1 reporter assay) REV-ERBα Kd = 0.8 μM (measured by circular dichroism binding assay) REV-ERBβ EC50 = 0.8 μM (measured by Gal4 reporter assay) Increases recruitment of CoRNR peptide fragment of NCOR Suppresses expression of REV-ERB target genes in vitro and in vivo Does not exhibit significant activity at other nuclear receptors (Gal4–UAS luciferase specificity panel) Causes loss of locomotor activity in the current circadian cycle after a single injection Causes weight loss in mice (due to decreased fat mass) without affecting food intake; increases oxygen consumption and decreases plasma lipids
|
105
|
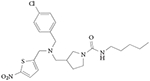
| SR9011 |
|
Agonist REV-ERBα EC50 = 0.79 μM (measured by Gal4 reporter assay) REV-ERBα EC50 = 0.62 μM (measured by full-length Bmal1 assay) REV-ERBβ EC50 = 0.56 μM (measured by Gal4 reporter assay) Suppresses expression of REV-ERB target genes in vitro and in vivo Increases recruitment of CoRNR peptide fragment of NCOR Does not exhibit significant activity at other nuclear receptors (measured by Gal4–UAS luciferase specificity panel) Suppresses the amplitude of circadian oscillations in SCN explants from a Per2-luciferase reporter mouse and in Per2-luciferase fibroblasts Causes loss of locomotor activity in the current circadian cycle after a single injection Causes weight loss in mice (due to decreased fat mass) without affecting food intake; increases oxygen consumption and decreases plasma lipids
|
105
|
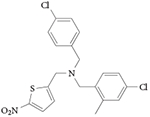
| GSK2945 |
|
REV-ERBα EC50 = 50 nM (measured by NCOR peptide recruitment) Reduces oscillation of BMAL-luciferase Inhibits IL-6 secretion Pharmacokinetics suitable for 20–30 mg per kg dosing daily
|
107
|
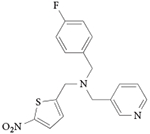
| GSK0999 |
|
REV-ERBα EC50 = 160 nM (measured by NCOR peptide recruitment) Reduces oscillation of BMAL-luciferase Inhibits IL-6 secretion Pharmacokinetics suitable for acute dosing
|
107
|
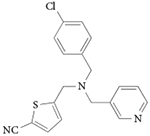
| GSK5072 |
|
REV-ERBα EC50 = 200 nM (measured by NCOR peptide recruitment) Reduces oscillation of BMAL-luciferase Inhibits IL-6 secretion Pharmacokinetics suitable for acute dosing
|
107
|
| GS2667 |

|
REV-ERBα EC50 = 200 nM (measured by NCOR peptide recruitment) Reduces oscillation of BMAL-luciferase Inhibits IL-6 secretion Pharmacokinetics suitable for acute dosing
|
107
|
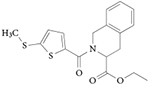
| SR8278 |
|
Antagonist REV-ERBα IC50 = 2.3 μM (measured using full-length Bmal1 reporter assay) Increases expression of REV-ERB target genes in cells Limited in vivo exposure, which limits its use as a chemical tool in vivo
|
108
|








