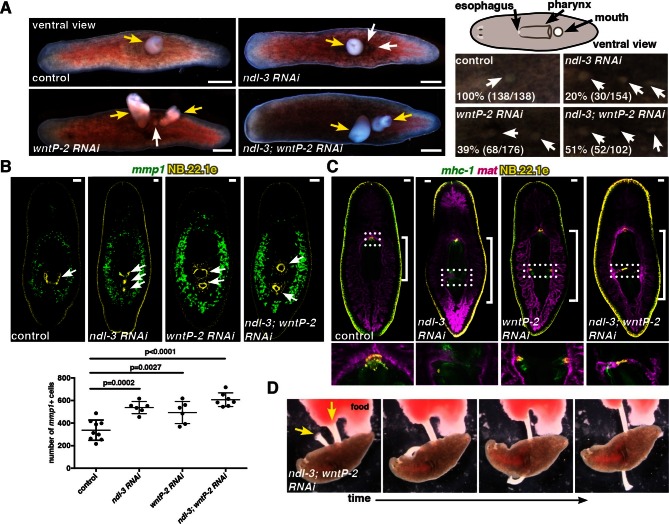
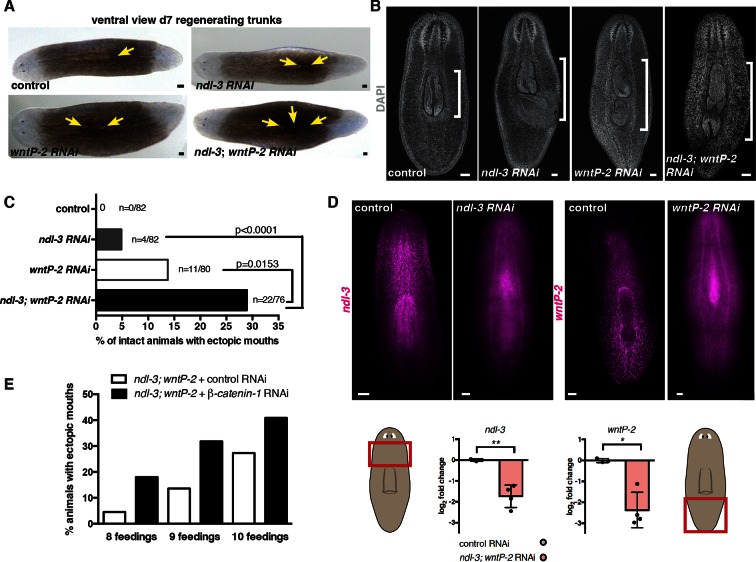
Figure 3. ndl-3 and wntP-2 restrict trunk positional identity.
(A) Live, ventral images of ectopic pharynges and mouths in 20–30 day post-amputation (dpa) RNAi animals. Right top, cartoon depicts esophagus, pharynx, and mouth. Left, pharynges (yellow arrows) and ectopic mouths without a protruding pharynx (white arrows). Scale bar, 500 μm. Right bottom, mouths (white arrows) in 7 dpa RNAi animals. Anterior, left. Total number of animals were pooled from at least 2 independent RNAi experiments. (B) Increased numbers of para-pharyngeal mmp1+ cells in RNAi animals. NB.22.1e labels mouths. Graph below shows mean ± SD (n>8 animals/condition, 2 pooled experiments, One-way ANOVA). (C) Esophagus-gut connection in 20 dpa trunk fragments, region in dotted rectangle is shown at higher magnification below. FISH: mat (gut), mhc-1 (pharynx), and NB.22.1e (esophagus). Bracket, pharyngeal cavity length. (D) Time-lapse images of an ndl-3; wntP-2 RNAi animal eating liver through both pharynges (yellow arrows), see Video 1.