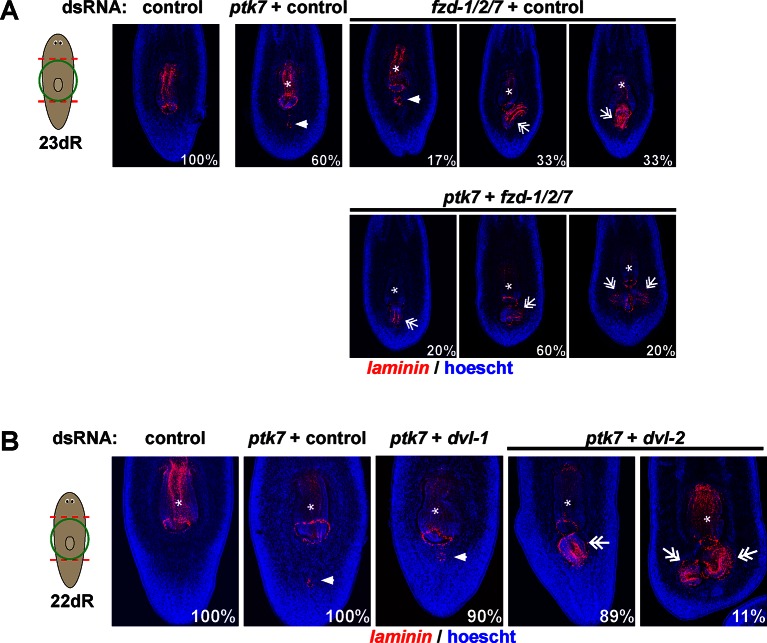
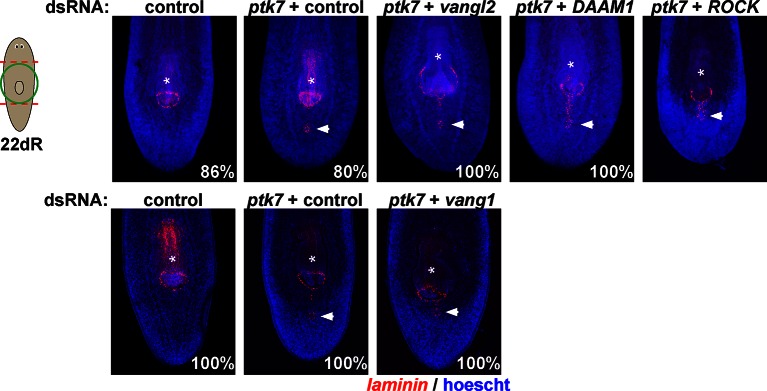
Figure 5. Trunk control genes likely signal independently of β-catenin-1.
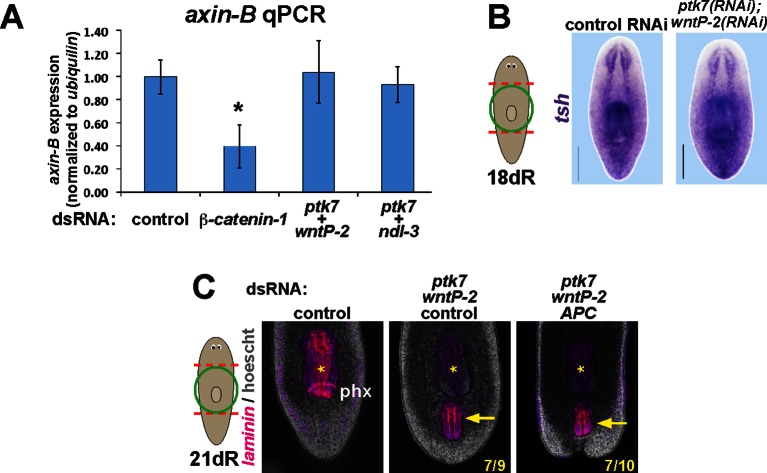
(A) In situ hybridizations show reduced expression of ptk7 (11/11 animals), wntP-2 (6/6 animals), and ndl-3 (6/6 animals) after 8 days (wntP-2, ndl-3) or 19 days (ptk7) of β-catenin-1 RNAi in uninjured animals. (B) In situ hybridizations showing reduction of axin-B expression after 11 days of β-catenin-1 RNAi (14/14 animals) but not after inhibition of wntP-2 and ptk7 (14/14 animals) or ndl-3 and ptk7 (14/14 animals). Bars, 400 microns.
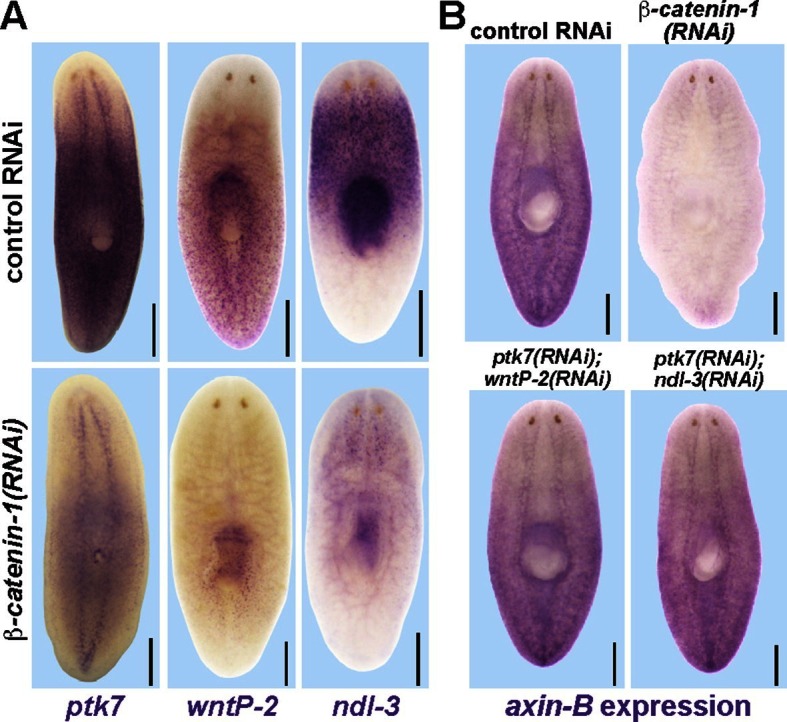
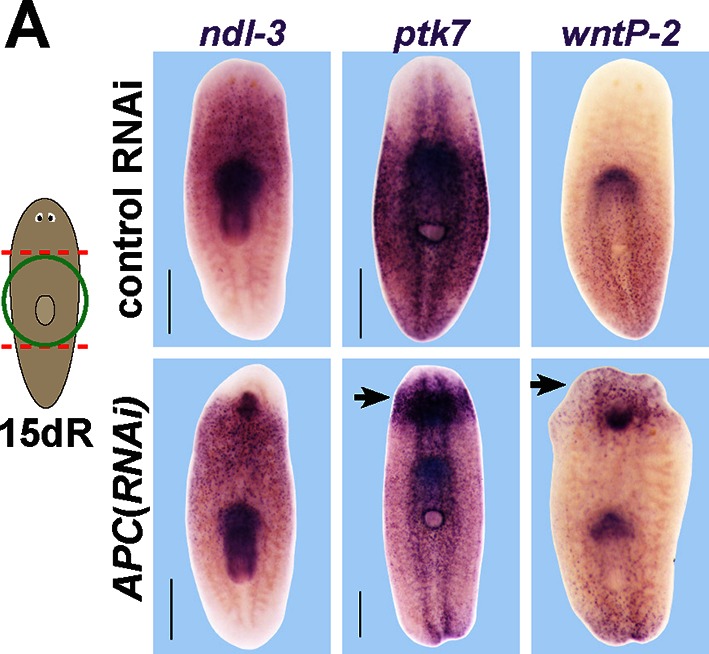
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Examining the effect of APC RNAi on expression of ptk7, wntP-2, and ndl-3.