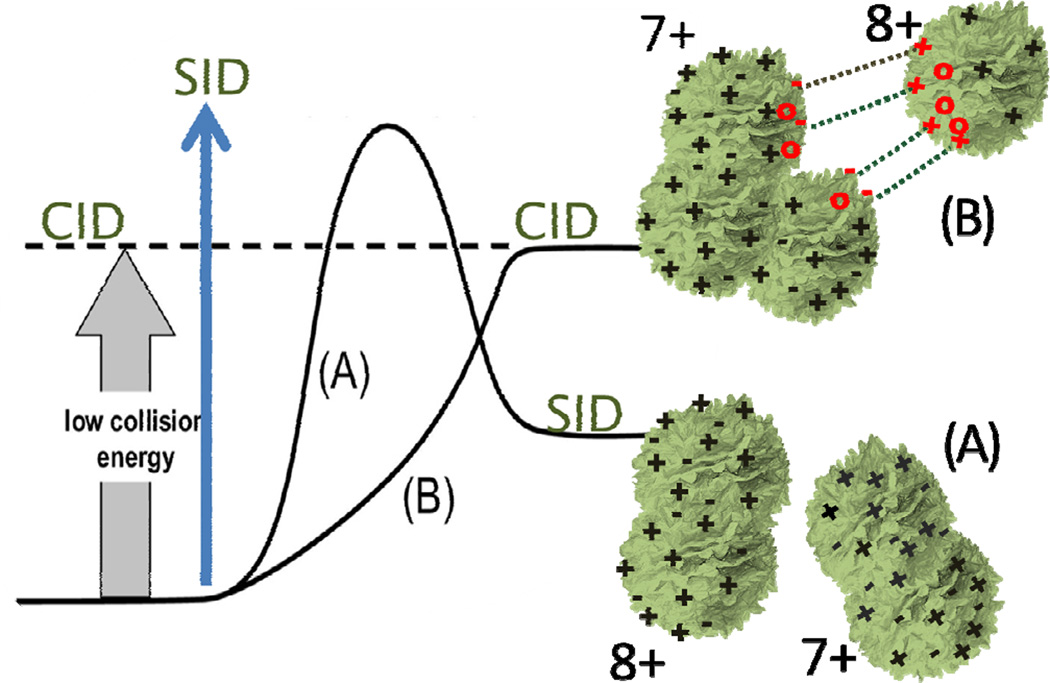
Figure 5.
Illustration of homolytic (A) and heterolytic (B) dissociation channels for a 15+ tetramer. Dissociation along thermodynamically favored channel A (homolytic) is accessible only at high collision energies, due to its electrostatic kinetic barrier. Low collision energy dissociations access the more endothermic, barrierless channel B.