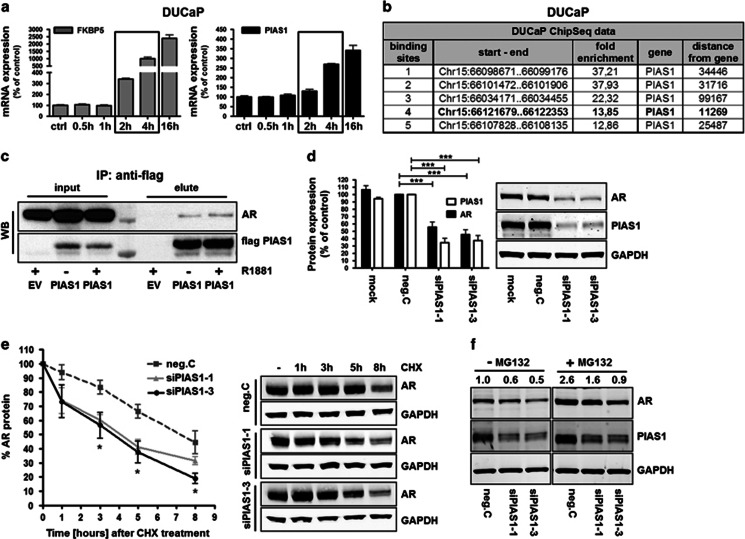
Figure 3.
PIAS1 binds and stabilizes AR and protects AR from proteasomal degradation. (a) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of DUCaP after treatment with R1881 (1 nM) for different durations, showing velocity of PIAS1 and FKBP5 mRNA transcription following AR activation. Data represent mean+s.e.m. from three independent experiments. (b) Analysis of ChIP-Seq data of DUCaP cells that were treated with vehicle or 1 nM of R1881 for 1 h24 shows AR enrichment sites in close proximity of the PIAS1 gene. (c) Western blot for AR and PIAS1 following co-immunoprecipitation of flag-PIAS1 and endogenous AR in DUCaP after transfection of 1 μg pFlag-PIAS1 or empty vector (EV) for 3 days in the absence or presence of R1881. (d) Western blot for AR and PIAS1 expression in DUCaP after transfection with control siRNA (neg.C) or PIAS1 siRNAs. Data represent mean+s.e.m. from three independent experiments (***P<0.001). (e) Velocity of AR degradation was measured in a time-course experiment by western blot after protein synthesis inhibition with cycloheximide (25 μg/ml) in control- or siPIAS1-transfected DUCaP cells. Data represent mean+s.e.m. from three independent experiments (*P<0.05 siPIAS1-1, siPIAS1-3 at 3 and 5 h; *P<0.05 siPIAS1-3 at 8 h). (f) Western blot for AR and PIAS1 in DUCaP cells that were transfected with control siRNA or PIAS1 siRNA for 72 h and subsequently treated with MG132 (25 μg/ml) for 8 h.