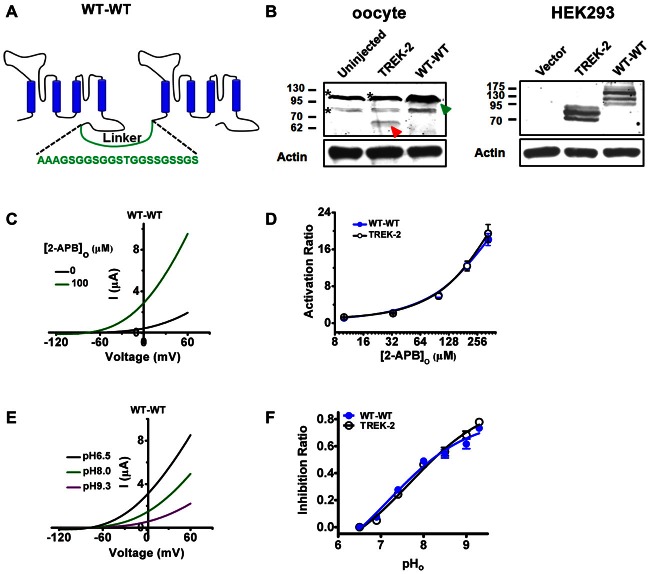
Figure 1.
Concatenated wild type (WT) TREK-2 dimers (WT-WT) functions similarly with their monomeric WT channels (TREK-2). (A) Diagram of concatenated TREK-2 dimer and the sequence of linker indicated. (B) Validation of TREK-2 and WT-WT proteins was tested by western blotting. cDNA encoding TREK-2 or WT-WT was injected into oocytes. The monomeric TREK-2 was indicated with red arrow, and the dimeric one with green arrow. *Indicates the nonspecific bands detected by the anti-TREK-2 primary antibody in oocytes (left panel). Constructs harboring GFP-tagged TREK-2 or WT-WT was transfected into HEK293 cells (right panel). (C) Exemplar current-voltage recordings from oocytes expressing the WT-WT channels in the presence of 100 μM 2-APB. The currents were elicited by continuous voltage-ramps from −120 to +60 mV from holding potential of −80 mV, with 2 s in duration. (D) Comparative analysis of the 2-APB evoked activation curves between TREK-2 and WT-WT channels. (E) Exemplar current-voltage recordings from oocytes expressing WT-WT channels as pHo transitions among 6.5, 8.0 and 9.3. (F) Concentration dependence of Inhibition ratio (IR) upon extracellular alkalization for TREK-2 and WT-WT channels.