Figure 3. Effect of Cx36 genotype on the asymmetry of electrical coupling in TRN .
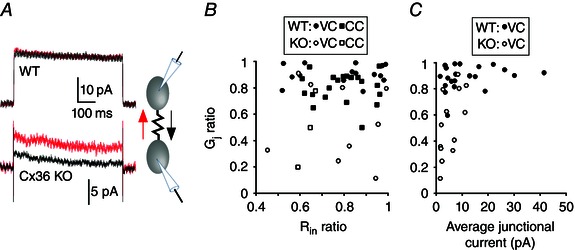
A, junctional currents induced by +80 mV and –80 mV transjunctional voltage steps (black and red traces, respectively). Junctional currents in the WT pair are similar in both directions. Junctional currents in the KO pair are direction‐dependent (i.e. asymmetric). B, relationship between junctional coupling asymmetry (G j ratio) and input resistance (R in ratio) among WT and KO neuron pairs. C, coupling asymmetry vs. mean coupling strength (pA) between WT and KO neuron pairs. Each symbol in (B) and (C) represents data from a neuron pair of the type as specified in the insets (VC, voltage clamp; CC, current clamp measurements).
