Figure 4. MC4R agonist inhibits Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV .
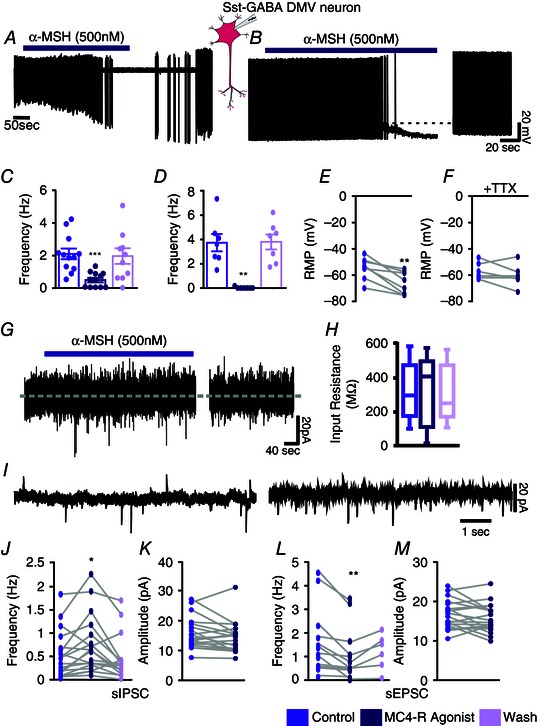
A, representative loose cell‐attached recording from a Sst‐GABA neuron and its inhibition by α‐MSH. B, representative current clamp recording from a Sst‐GABA neuron in the absence and presence of α‐MSH. C and D, summaries of the effects of α‐MSH on action potential frequency in Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV in the cell‐attached (n = 12; ***P < 0.001) and current clamp modes (n = 7; **P < 0.01), respectively. E and F, summaries of the effects of α‐MSH on resting membrane potential (RMP) in Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV (n = 8; **P < 0.01) in the absence (E) and presence (F) of TTX (n = 6, P > 0.05). G, representative voltage clamp recording showing direct membrane current or input resistance (H) α‐MSH. I, representative voltage clamp recording (V H = −30 mV) showing sPSCs before (left) and during (right) exposure to α‐MSH. J, α‐MSH increases sIPSC frequency of Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV (n = 16; **P < 0.01). K, sIPSC amplitude of Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV is unaffected by α‐MSH (n = 18). L, α‐MSH decreases the sEPSC frequency of Sst‐GABA neurons in the DMV (n = 17; **P < 0.01) but has no effect (M) on sEPSC amplitude (n = 19).
