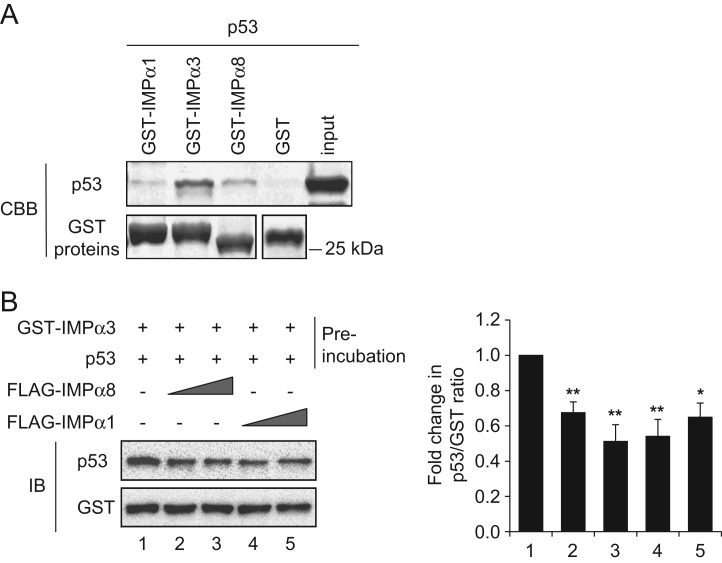
Fig. 2.
Either importin α8 or α1 dissociates the importin α3-p53 complex by dimer formation with importin α3. (A) p53 preferentially binds to importin α3 rather than importin α1 or α8. Pull-down assays were performed with the p53 recombinant protein and with GST-importin α1 (IMPα1), GST-importin α3 (IMPα3), or GST-importin α8 (IMPα8) immobilized on GSH beads. After incubation at 4 °C for 1 h, the beads were washed and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Proteins are detected by Coomassie staining. p53 (10 pmol) was loaded as an input control. (B) GST-importin α3 (IMPα3) immobilized on GSH beads was preincubated with a five times higher amount of p53 to form a complex (Preincubation). Then, increasing amounts of FLAG-importin α8 or FLAG-importin α1 (equal or 10 times higher amount than GST-IMPα3) were added. Bound proteins were analyzed by western blotting using the antibodies indicated. Left panels: representative immunoblot images of the p53 and GST-importin α3 bands. Right panels: relative fold changes in the p53/GST ratio in the presence of either FLAG-importin α8 or FLAG-importin α1, which were normalized to the control condition (without FLAG-importin αs). The results are from three independent experiments and have been presented as mean ± SEM. The numbers 1–5 correspond to the lane numbers described in the left panels. **p<0.01, *p<0.05; Student׳s t-test.