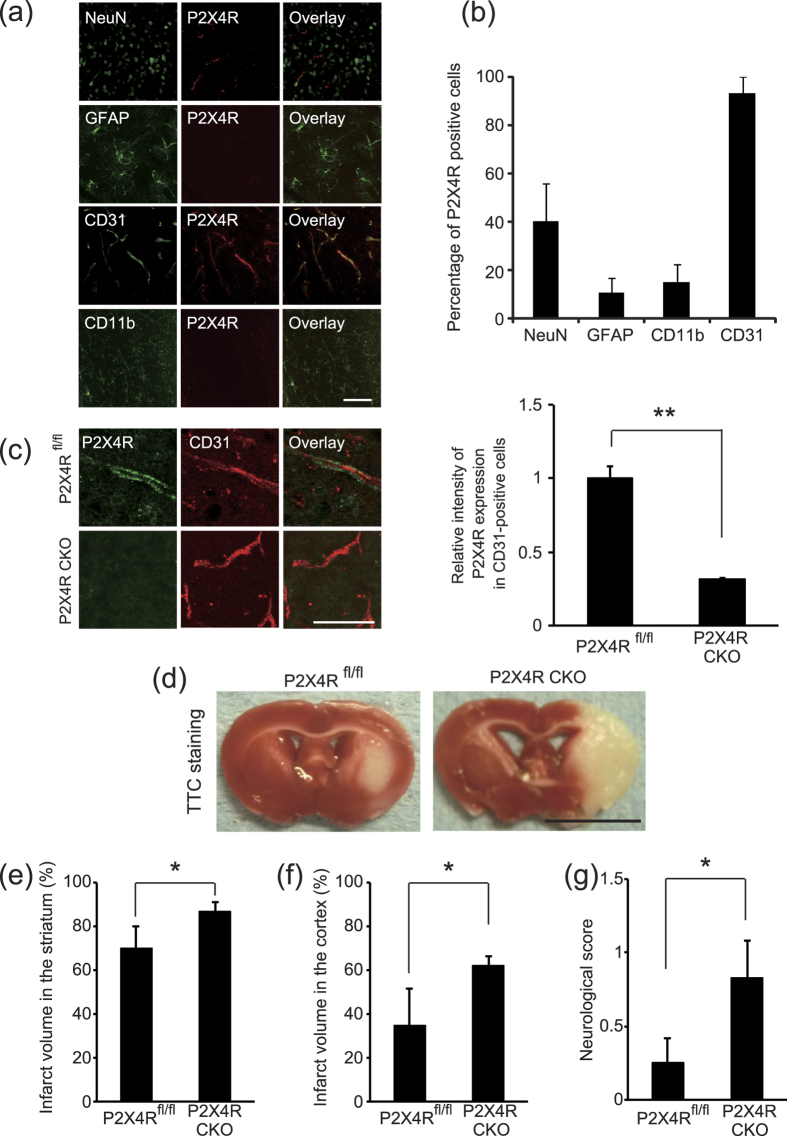
Figure 2. P2X4 receptor expression in vascular endothelial cells is required for neuroprotection after MCAO.
(a) Immunostaining for P2X4 receptor expression (Alexa Fluor 568) in combination with NeuN, GFAP, CD31, and CD11b (Alexa Fluor 488) in brain sections from intact mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Quantification of P2X4 receptor expression in indicated cell marker-labeled cells. The data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3). (c) Relative intensity of P2X4 receptor protein in CD31-positive cells obtained from the indicated mice treated with tamoxifen (p = 0.0006, **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test). Scale bar, 50 μm. Graph shows the intensity of P2X4 receptor expression in CD31-positive cells. The data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3). (d) Representative images of TTC-stained brain slices obtained 24 hr after MCAO. P2X4R fl/fl mice or P2X4R conditional knockout mice (CKO) were subjected IPC 48 hr before MCAO. Bar, 5 mm. (e,f) Graphs show the percentage of infarction (infarct ratio) in the ipsilateral striatum (e) and cortex (f). Genetic ablation of P2X4 receptor in VE-cadherin-positive cells prevented IPC-mediated neuroprotection after prolonged MCAO (striatum p = 0.0497, cortex p = 0.0442, *p < 0.05, ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer test). The data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (+/+:: flox/flox, n = 4; cre/+:: flox/flox, n = 6). (g) P2X4 receptor expression in VE-cadherin-positive cells decreased IPC-prevented neurological deficits caused by MCAO (p = 0.0383, *p < 0.05, ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer test). The data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (+/+:: flox/flox, n = 4; cre/+:: flox/flox, n = 6).