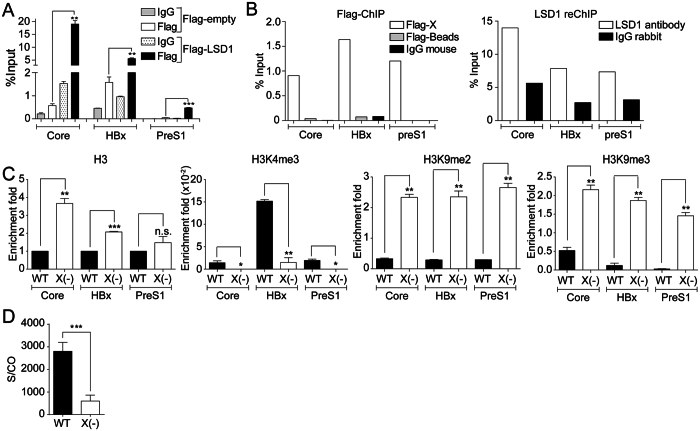
Figure 5. LSD1 is recruited to HBV promoters in an HBx-dependent manner.
(A) Human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells were transfected with the wild type HBV genome together with either a plasmid encoding for a Flag-tagged LSD1 or a Flag protein as a control. Flag-LSD1 recruitment to viral promoters was assayed by ChIP analysis. Immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by qPCR using specific primers as detailed in Material and Methods. The results are expressed as % of input. The standard deviation was obtained from three independent experiments. (B) Human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells were transfected with the wild type HBV genome together with either a plasmid encoding for a Flag-tagged HBx or a Flag protein as a control. Flag-HBx recruitment to viral promoters was assayed by ChIP analysis (left). Then the Flag-HBx immunoprecipitated samples were reChIP with antibodies against LSD1 or IgG antibodies as control (right). Immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by qPCR using specific primers as detailed in Material and Methods. The results are expressed as % of input. (C) Covalent post-translational modifications on histone H3 were determined by ChIP analysis using the specific antibodies, as indicated. Immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by qPCR using specific primers as detailed in Material and Methods. When analyzing histone modifications, we normalized the data against the immunoprecipitated H3. The standard deviation was obtained from three PCR reactions and the graphs are representative of three independent experiments. (D) The quantity of viral antigens in the supernatant of WT and HBV- transfected cells after 72 h was determined by ELISA, using specific antibodies against the HBs protein. In each case, the results are presented as a signal-to-cutoff (S/CO) ratio. The standard deviation was obtained from four independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student´s t-test.