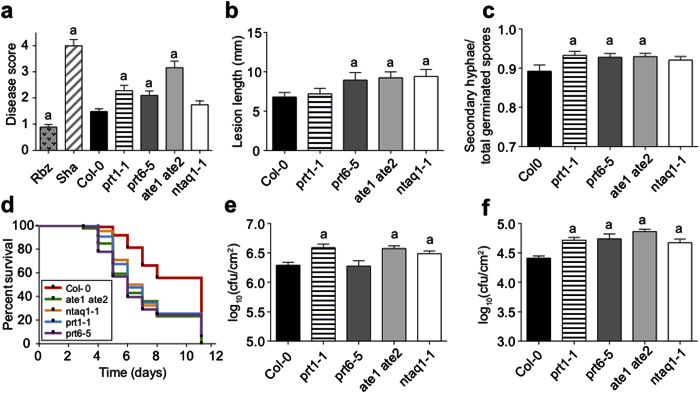
Figure 4. N-end rule mutants are more susceptible to pathogens with different lifestyles.
(a) Results of susceptibility tests with the necrotrophic fungus S. sclerotiorum. Seven days post-inoculation with S. sclerotiorum, plants were scored as described in the Methods section. Means and SEM were calculated from scoring three independent experiments. The Shahdara (Sha) and Rubezhnoe (Rbz) accessions were used as susceptible and resistant control plants, respectively. (b) Lesion length four days following inoculation with the necrotrophic fungus B. cinerea. Means and SEM were calculated from scoring four independent experiments. (c) Results of susceptibility tests after inoculation with the obligate biotrophic fungus E. cruciferarum. The ratio of secondary hyphae formed relative to the total number of germinated spores was calculated two days post-inoculation. Means and SEM were calculated from four independent experiments. (d) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of the indicated lines inoculated with the strain GMI1000 of R. solanacearum. The graph shows pooled results from four independent experiments (20-25 plants/experiment/line). P-values (<0.0001) from Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon tests are associated with each graph. (e) Bacterial counts three days post-inoculation with virulent Pst DC3000 (1 × 105 cfu/mL). Mean bacterial densities and SEM were calculated from six independent experiments. (f) Bacterial counts three days post-inoculation with avirulent Pst AvrRpm1 (5 × 105 cfu/mL). Mean bacterial densities and SEM were calculated from five independent experiments. Statistical significance is indicated with ‘a’, based on the tests described in the Methods section.