Figure 2. GNF-2 analogs that lack activity against Abl kinases.
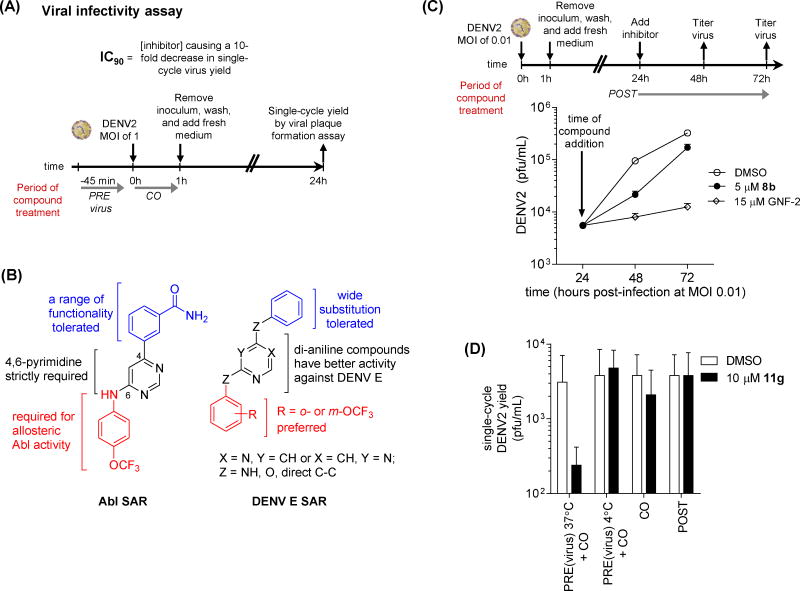
inhibit DENV via (A) Schematic of viral infectivity assay measuring the antiviral activity exerted by compounds when preincubated with viral inoculum at 37 degrees C, 45 minutes and when present during the one hour incubation of cells with the viral inoculum but absent for the remainder of the experiment. Single-cycle viral yield was quantified at 24 hpi as a readout for inhibition of viral infectivity during the initial infection. (B) Summary of structure-activity relationships (SAR) distinguishing inhibition of Abl kinases and antiviral activity measured in the viral infectivity assay. While trends for anti-DENV activity are derived from data against all four DENV serotypes as listed in Tables 1 and S1, the observed trends are most robust for DENV2 and DENV1. (C) Both GNF-2 and 8b inhibit DENV2 in a low multiplicity of infection (MOI 0.01), multiple replication cycle experiment when inhibitor treatment is delayed until 24 hpi. Culture supernatants were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi to allow quantification of viral titers and demonstration of antiviral activity. (D) Inhibition of DENV2 in the viral infectivity assay (Figure 2A) is lost if incubation of inhibitor with viral inoculum is performed at 4 degrees C. Data are shown for compound 11g; analogous experiments were performed for other analogs in Table 1. Each experiment was performed n ≥ 2, and viral plaque formation assays were performed in triplicate (A, D) or duplicate (C). Representative data are shown for the mean ± stdev of the viral plaque formation assays for a representative experiment.