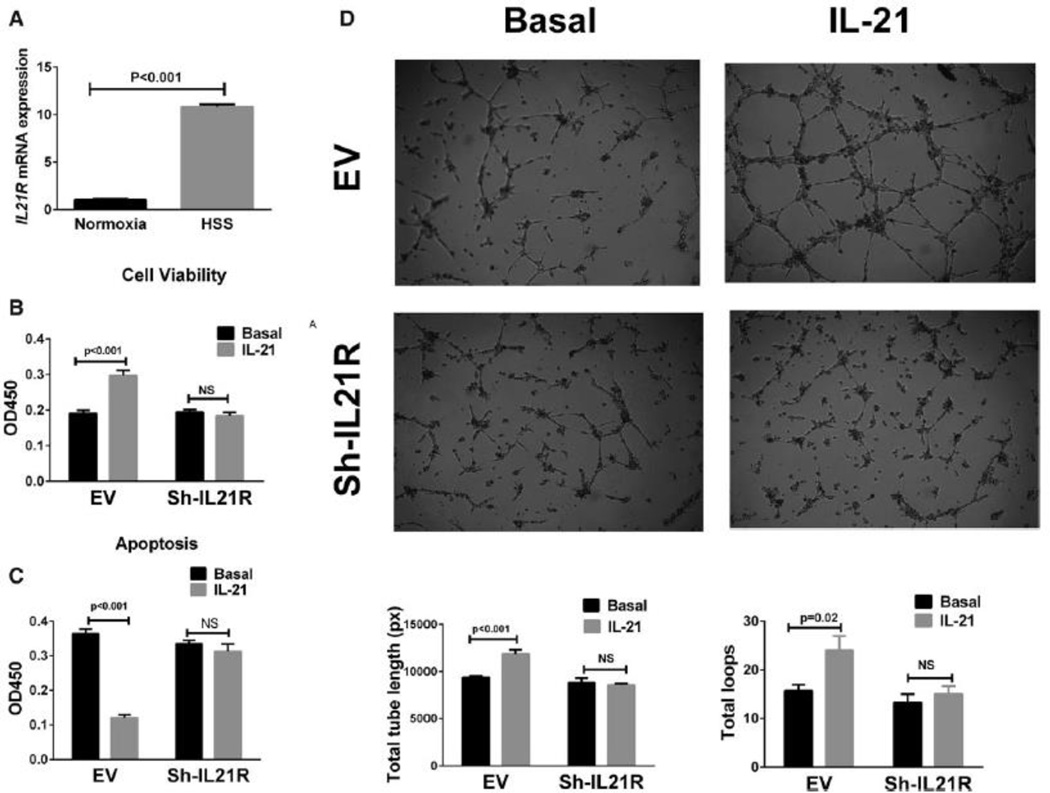
Figure 2. IL-21R expression and the effect of IL-21 treatment in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
(A) Following 24 hours of hypoxia and serum starvation (HSS), qPCR showed ~10-fold increase in il21R mRNA expression when compared to HUVECs cultured under normoxia (normoxia indicates cells cultured under normal condition). (B) More viable cells were detected with 24h after IL-21 (50 ng/mL) treatment for in HSS conditions. Cell viability assay is based on the cleavage of the tetrazolium salt to formazan by cellular mitochondrial dehydrogenase. (C) In situ terminal dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) showed that IL-21 (50 ng/mL) treatment for 24h decreases HUVEC cell apoptosis in HSS conditions. (D) HUVECs were plated on matrigel with reduced growth factor and incubated for 10 hours in HSS conditions with basal or treatment medium, IL-21 treated HUVECs showed enhanced tube formation, which was quantified as total length of the cords per visual filed, and total loops per visual field as represented by the bar graph. The lL-21 effects on HUVECs viability, apoptosis and tube formation (B-D) were inhibited when IL-21R expression was knocked down by using shRNA. All the above data are representative of 2–3 separate batches of HUVECs, n = 8–12 samples/group.