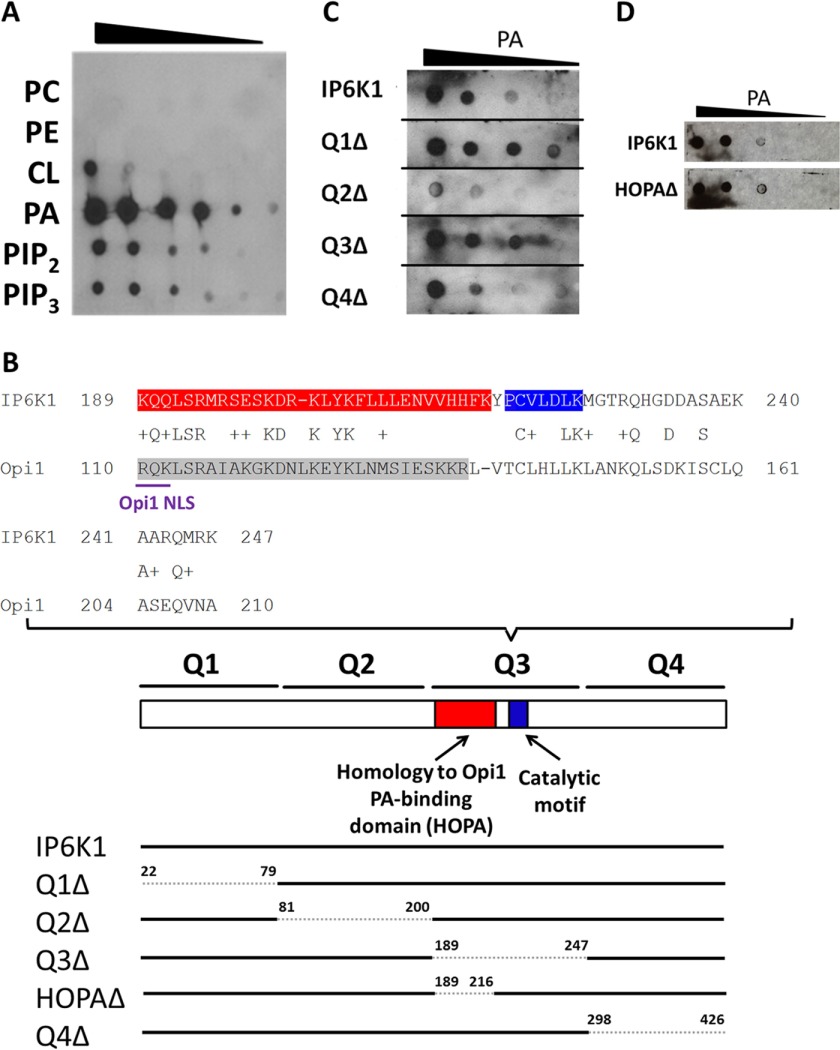
FIGURE 4.
IP6K1 binds preferentially to PA. A, IP6K1 protein was purified from E. coli cells expressing the Ip6k1 gene on the pGEX-6-P2 overexpression vector. Serial dilutions of the indicated lipids were spotted on a nitrocellulose membrane, which was incubated overnight in buffer containing 25 μg of IP6K1 protein. Interactions between IP6K1 and lipids were determined by immunoblotting, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, IP6K1 exhibits sequence homology to yeast Opi1 (upper panel). The IP6K1 HOPA domain, which exhibits homology to the PA-binding domain of yeast Opi1, is highlighted in red. The catalytic motif of IP6K1 is highlighted in blue. The PA-binding domain of yeast Opi1 is highlighted in gray. The NLS of yeast Opi1 is underlined in purple. IP6K1 deletion mutants were constructed by site-directed mutagenesis according to the schematic figure (lower panel). Residues deleted are indicated by numbers above the bar. C, deletion of the Q2 domain of IP6K1 decreased binding to PA. WT and mutant IP6K1 proteins were overexpressed and purified from E. coli. Interactions between protein and PA were determined as described previously. Figure represents three independent experiments. D, deletion of the HOPA domain of IP6K1 did not affect binding to PA. WT and HOPAΔ IP6K1 proteins were expressed and purified from E. coli. Interactions between protein and PA were determined as described previously.