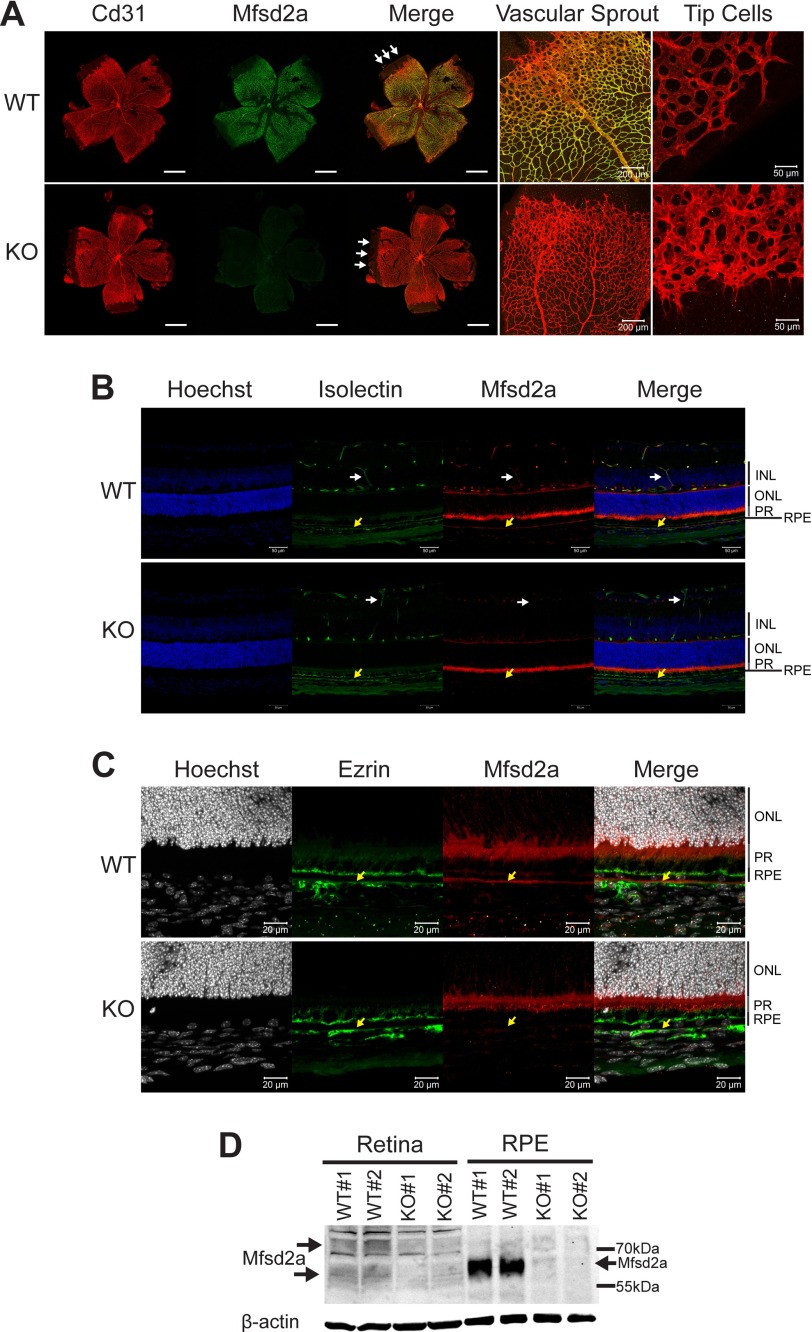
FIGURE 1.
Mfsd2a is expressed in retinal vessels and RPE. A, immunolocalization of Mfsd2a in capillaries of the developing eye. Retinal whole mounts were prepared from postnatal day 8 wild-type (WT) and Mfsd2a deficient (KO) mice and stained for the endothelial cell marker Cd31 and Mfsd2a. Mfsd2a KO served as a negative control for Mfsd2a antibody specificity. Endothelial tip cells are seen at the leading edge of the growing vasculature sprouts (white arrows). Mfsd2a is shown to be expressed only in mature capillaries but is absent in tip cells. WT, n = 4; KO, n = 4; scale bar = 1 mm. B, cross-sections of eyes of postnatal day 14 (P14) mice were stained for isolectin, an endothelial marker, Mfsd2a, and Hoechst (a nuclear stain). Co-expression is seen in the capillaries (white arrow) and RPE (yellow arrow). Autofluorescence is observed in photoreceptor outer segments. WT, n = 5; KO, n = 5; scale bar, 50 μm. C, to confirm Mfsd2a expression in the RPE, eye sections from P14 mice were stained for ezrin, an apical and basolateral membrane marker in RPE, and Mfsd2a, and Hoechst (a nuclear stain). Co-expression is seen at the basolateral membrane (yellow arrow). Autofluorescence is observed in photoreceptor outer segments. WT, n = 5; KO, n = 5; scale bar, 20 μm. D, representative Western blot of Mfsd2a expression in 80 μg of retina and 8 μg of RPE (eye cup without retina) in 8-week-old mice. Mfsd2a is more abundantly expressed in RPE relative to the retina. β-Actin served as a loading control. WT, n = 4; KO, n = 4. INL, inner nuclear layer; PR, photoreceptor.