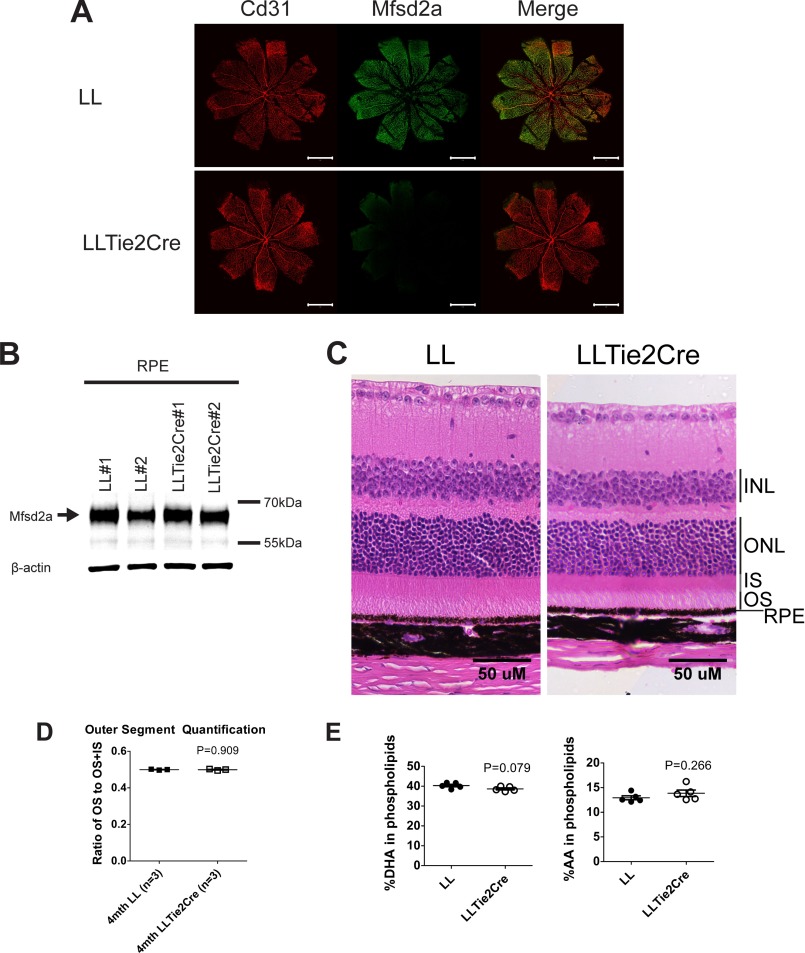
FIGURE 8.
Mfsd2a deficiency in retina vasculature does not contribute to eye DHA accretion or photoreceptor survival. A, immunolocalization of Mfsd2a in capillaries of the developing eye. Retinal whole mounts were prepared from postnatal day 9 Mfsd2a floxed (LL) and LLTie2Cre mice and stained for the endothelial cell marker Cd31 and Mfsd2a. Mfsd2a is shown to be expressed only in capillaries of LL mice but absent in LLTie2Cre mice, consistent with deletion in retina vasculature. Scale bar, 1 mm. LL, n = 2; LLTie2Cre, n = 2. B, representative Western blot of Mfsd2a expression in RPE (eye cup without retina) of 6-week-old mice. As expected, Mfsd2a levels are similar between LL and LLTie2Cre RPE. β-Actin served as a loading control. LL, n = 2; LLTie2Cre, n = 2. C, H&E staining of eyes of 4-month-old mice was carried out to visualize the layers. Although eyes of LLTie2Cre mice appear slightly smaller, retina layers appear comparable with LL control. LL, n = 3; LLTie2Cre, n = 4. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, ratio of OS to OS + IS was quantified in eyes of 4-month-old mice. Ratios of OS length are comparable between eyes of LL and LLTie2Cre mice. LL, n = 3; LLTie2Cre, n = 3. E, comprehensive lipidomic analysis of whole eyes from 7-week-old mice. Total DHA and AA levels in eye phospholipids are expressed as mean ± S.E. of the percentage of the total level of phospholipids. LL, n = 5; LLTie2Cre, n = 5.