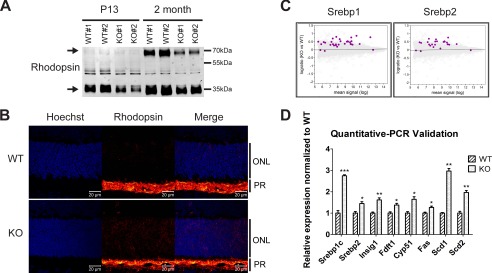
FIGURE 9.
Mfsd2a deficiency results in reduced rhodopsin levels and mislocalization and up-regulation of lipogenesis pathways. A, representative Western blot of rhodopsin expression in whole eyes in P13 and 2-month-old mice. Reduced rhodopsin expression is seen in Mfsd2a KO mice as early as P13. Black arrows indicate monomeric and dimeric rhodopsin. P13, n = 2 per genotype; 2-month-old mice, n = 4 per genotype. B, immunolocalization of rhodopsin was performed on eye sections from P14 mice. Rhodopsin, which normally resides in the OS, as seen in WT, was found to be mislocalized to the ONL layer in Mfsd2a KO retina. Scale bar, 20 μm. WT, n = 5; KO, n = 5. C, gene microarray analysis from P13 eye cups of WT and Mfsd2a KO mice. An MA plot, which is used to visualize intensity-dependent ratio of raw gene microarray data, indicated that the top predicted up-regulated genes in Mfsd2a KO eyes are the lipogenic and cholesterogenic Srebp1 and Srebp2 pathways, respectively. Purple dots on each graph represent individual Srebp1 and Srebp2 targets over the background of expressed genes. D, quantitative-PCR was carried out on selected panel to validate gene array findings. WT, n = 4; KO, n = 4. ***, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. PR, photoreceptor.