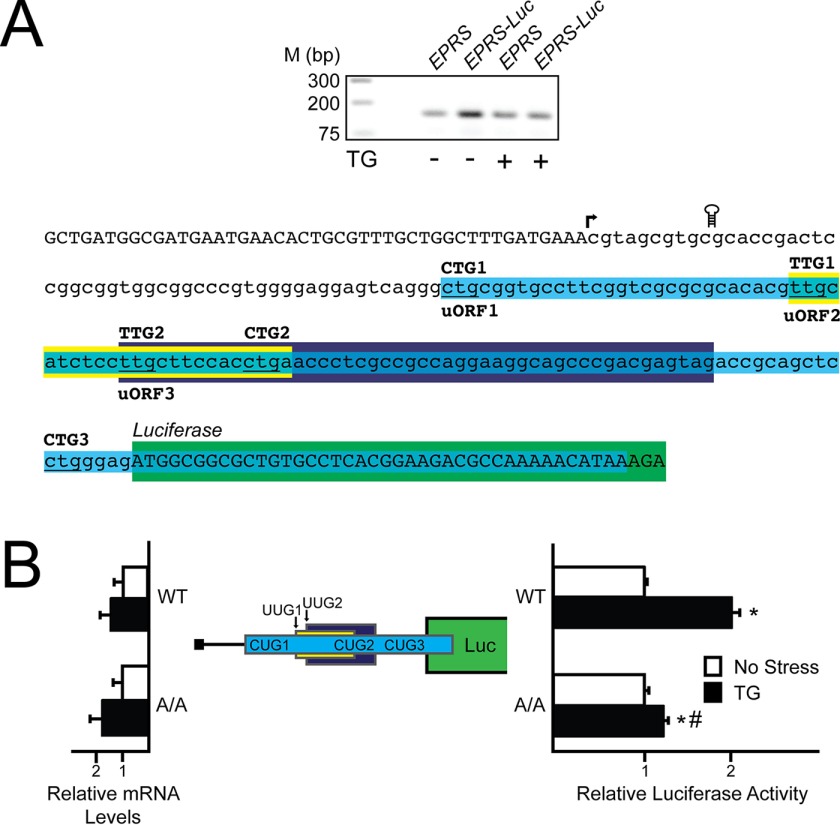
FIGURE 2.
The 5′-leader of the EPRS mRNA directs preferential translation. A, top panel, a 5′-RACE was conducted for EPRS using WT MEFs treated with thapsigargin for 6 h or left untreated. Total RNA and cDNA were prepared, and DNA products were separated by gel electrophoresis, with markers for the indicted base pair sizes listed on the left. Bottom panel, nucleotide representation of the EPRS 5′-leader in lowercase letters, with uppercase letters representing the 5′-linker added during the 5′-RACE procedure and the beginning of the CDS of the EPRS-Luc fusion. Colored boxes represent the EPRS uORFs, with uORF1 in blue, uORF2 in yellow, and uORF3 in purple. Start codons for each uORF are indicated above the colored boxes. The coding region of the EPRS-Luc fusion is illustrated by the green box. The transcription start site is indicated with an arrow, and the location of the stem loop insertion is illustrated. B, the PTK-EPRS-Luc construct and a Renilla luciferase reporter were co-transfected into WT or A/A MEFs and treated with thapsigargin for 6 h or left untreated. EPRS 5′-leader mediated translation control was measured via Dual-Luciferase assay, and the corresponding EPRS-Luc mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. The PTK-EPRS-Luc construct contains the cDNA sequence corresponding to the EPRS 5′-leader fused to the luciferase reporter gene with both the EPRS uORFs and the CDS of the EPRS-Luc fusion indicated with colored boxes that are the analogues to those indicated in Fig. 2A. TG, thapsigargin; Luc, luciferase.