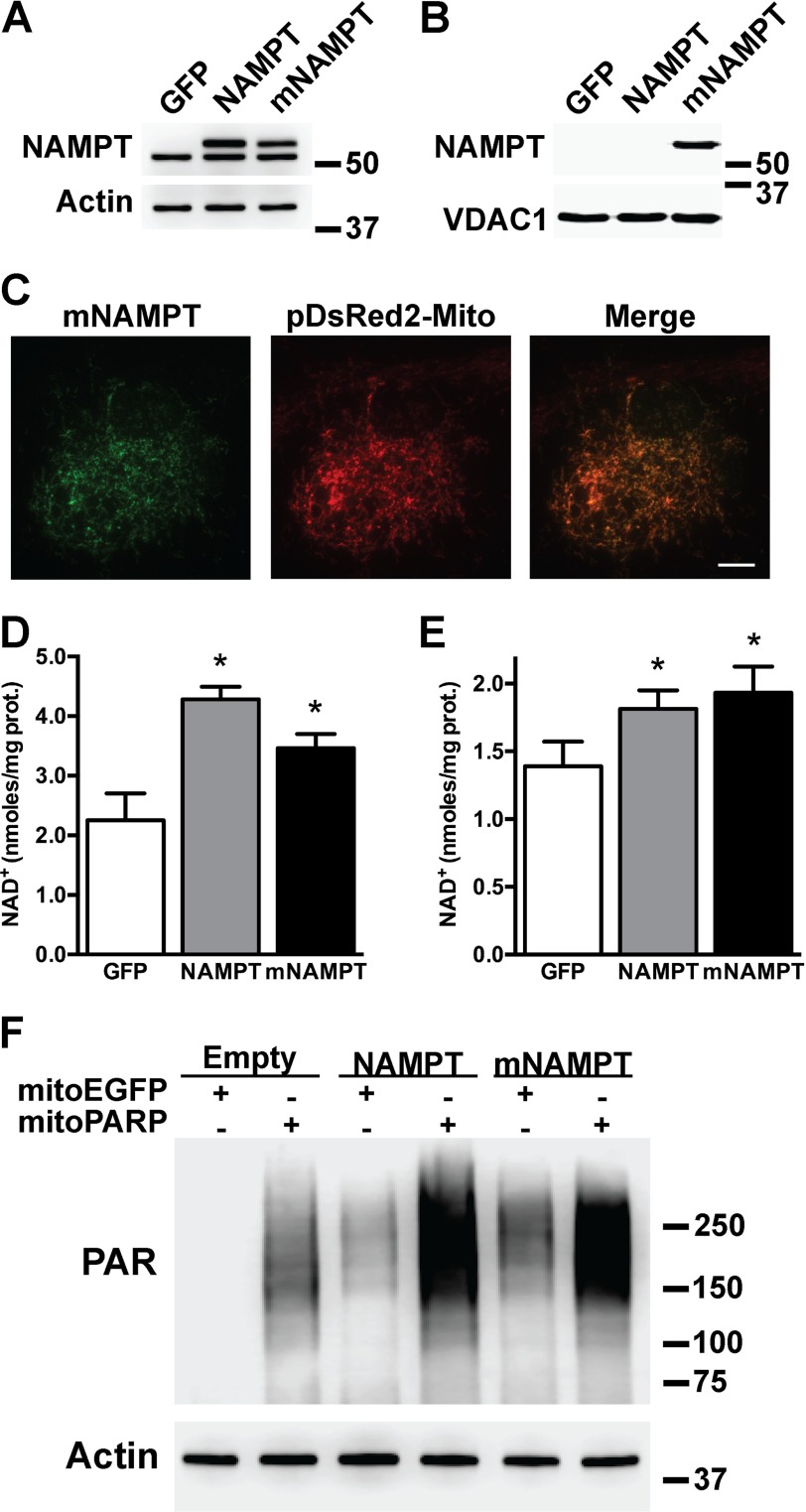
FIGURE 2.
A mitochondrially targeted NAMPT increases total and mitochondrial NAD+ content in astrocytes. Primary confluent spinal cord astrocytes were transfected with adenovirus expressing GFP, NAMPT, or mNAMPT. 48 h post-transfection NAMPT protein levels were determined by Western blotting in whole (A) or purified mitochondrial fractions (B). Actin or VDAC1 levels were used as loading controls. C, micrographs showing co-localization of mNAMPT (anti-DDK antibody; green) and a red fluorescent protein targeted to the mitochondria (pDsRed2-Mito; red) in spinal cord astrocytes co-transfected with vectors coding for mNAMPT and pDsRed2-Mito. Scale bar, 8 μm. Total (D) and mitochondrial (E) NAD+ content in spinal cord astrocyte cultures 48 h after transfection with adenovirus expressing GFP, NAMPT, or mNAMPT was determined. NAD+ was determined as described under “Experimental Procedures” and corrected by protein (prot.) content. Each data bar represents the mean ± S.D. (error bars) of at least three independent experiments. *, significantly different from GFP (p < 0.05). F, increased mitochondrial NAD+ content in HEK293 cells evidenced by PAR polymer accumulation mediated by a mitochondrially targeted PARP1 catalytic domain following co-expression of NAMPT and mNAMPT. HEK293 cells stably transfected with a mitochondrially targeted EGFP (mitoEGFP) or mitoPARP were transient transfected with NAMPT, mNAMPT, or empty plasmids. 24 h post-transfection PAR polymer accumulation was determined by Western blotting. Actin levels were used as a loading control.