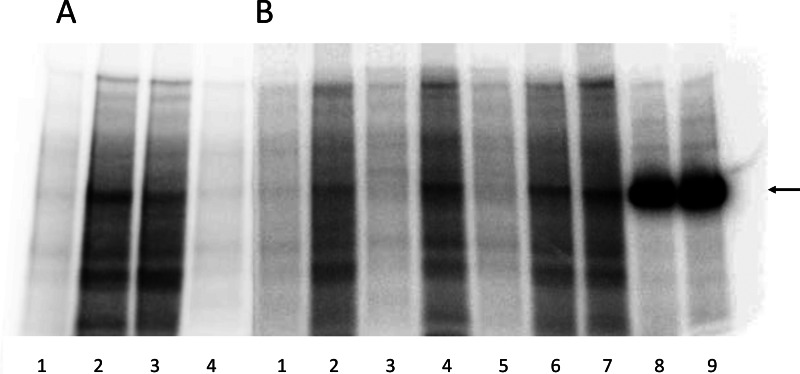
FIGURE 6.
PKA-mediated phosphorylation of Na+,K+-ATPase mutants. Representative phosphorimaging autoradiographs showing 32P incorporation following incubation with [γ-32P]ATP with PKA or without PKA catalytic subunit and separation by SDS-PAGE of COS-1 cell plasma membrane proteins containing expressed Na+,K+-ATPase mutants or wild type (WT) or purified Na+,K+-ATPase from pig kidney. See “Experimental Procedures” for further details. Two SDS-PAGE gels, A and B, are shown. A, lane 1, WT − PKA; lane 2, WT + PKA; lane 3, S938A + PKA; lane 4, S938A − PKA. B, lane 1, S938A − PKA; lane 2, S938A +PKA; lane 3, R1005A − PKA; lane 4, R1005A + PKA; lane 5, R1005K − PKA; lane 6, R1005K + PKA; lane 7, R1005M + PKA; lane 8, purified Na+,K+-ATPase (15 μg) +PKA; lane 9, purified Na+,K+-ATPase (20 μg) + PKA. The arrow indicates the migration position corresponding to the purified Na+,K+-ATPase. For both gel A and gel B, 35 μg of total plasma membrane protein from COS-1 cells expressing mutant or wild type were loaded in each lane. Plasma membrane preparations containing approximately equal amounts (±5%) of expressed exogenous mutant or wild type rat Na+,K+-ATPase per mg of total protein were used based on determination of the active site concentration.