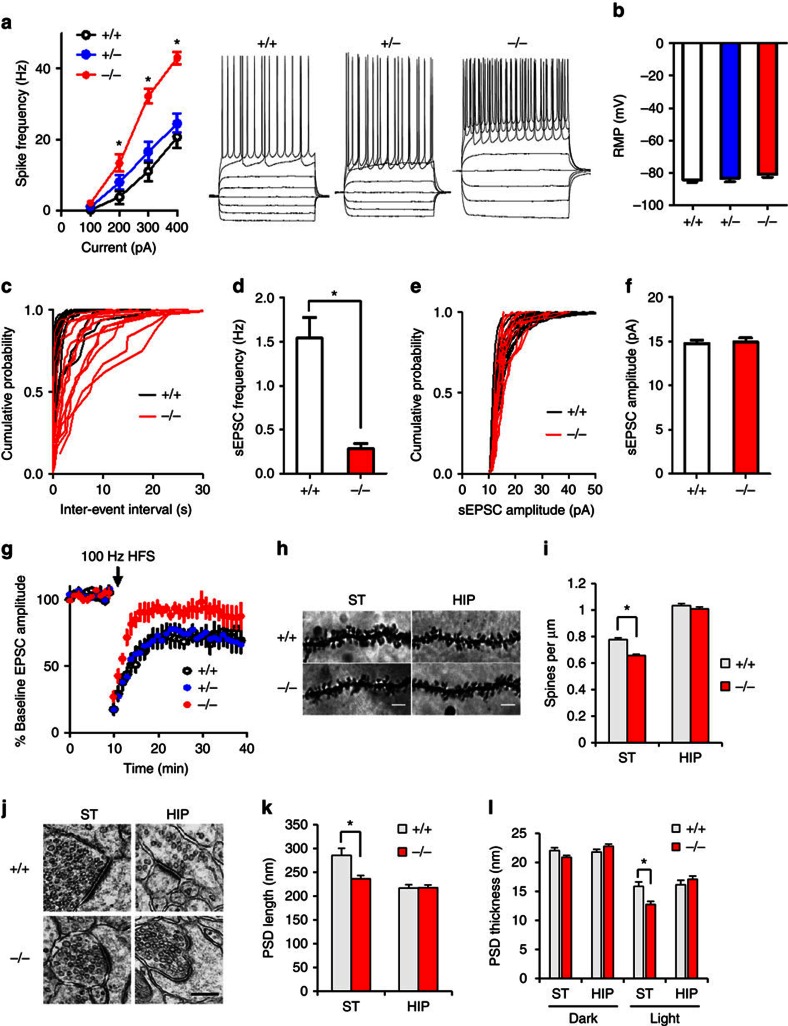
Figure 5. Electrophysiological characterization of striatal medium spiny neurons in Δe4–22 mice.
(a) Spike frequency in response to current injection. Δe4–22−/− (−/−) neurons showed enhanced excitability with 200–400 pA injected current (*P<0.05) compared with Δe4–22+/− (+/−) and Δe4–22+/+ (+/+) neurons (F(3, 267)=242.8, P<0.0001); n=28–32 neurons/genotype. (b) No genotype differences in RMPs were observed; n=28–32/genotype. (c,d) The frequency of sEPSCs was significantly reduced in −/− neurons; *P<0.001, t-test, n=13–14/genotype. (e,f) The sEPSC amplitude was not altered in −/− neurons; n=13–14/genotype. (g) HFS-induced LTD was impaired in −/− neurons; (planned comparison, t-test, P<0.05 for mice +/+, P<0.01 for +/−, and p>0.05 for −/− mice; n=8–12/genotype). (h) Sample images of Golgi-impregnated neurons in striatum (ST) and CA1 area of hippocampus (HIP) from −/− and +/+ mice. Scale bar: 5 μm. (i) A decrease in spine density was found in striatum of −/− mice. *P<0.001, t-test, n=97 branches from 50 cells of three mice/genotype. (j–l) Altered PSD ultrastructure in −/− mice. (j) Representative images for EM from striatum and CA1 hippocampus. Scale bar, 0.2 μm. (k) The PSD length was significantly decreased in striatum. (l) The PSD is thinner in striatum, especially its cytoplasmic ‘light' portion. *P<0.005, t-test. n=79 synapses from 4 +/+ mice and n=139 synapses from 6 −/− mice for striatum; n=120 synapses from 6 +/+ mice and n=148 synapses from 6 −/− mice for hippocampus. All data are expressed as means±s.e.m. RMP, resting membrane potential.