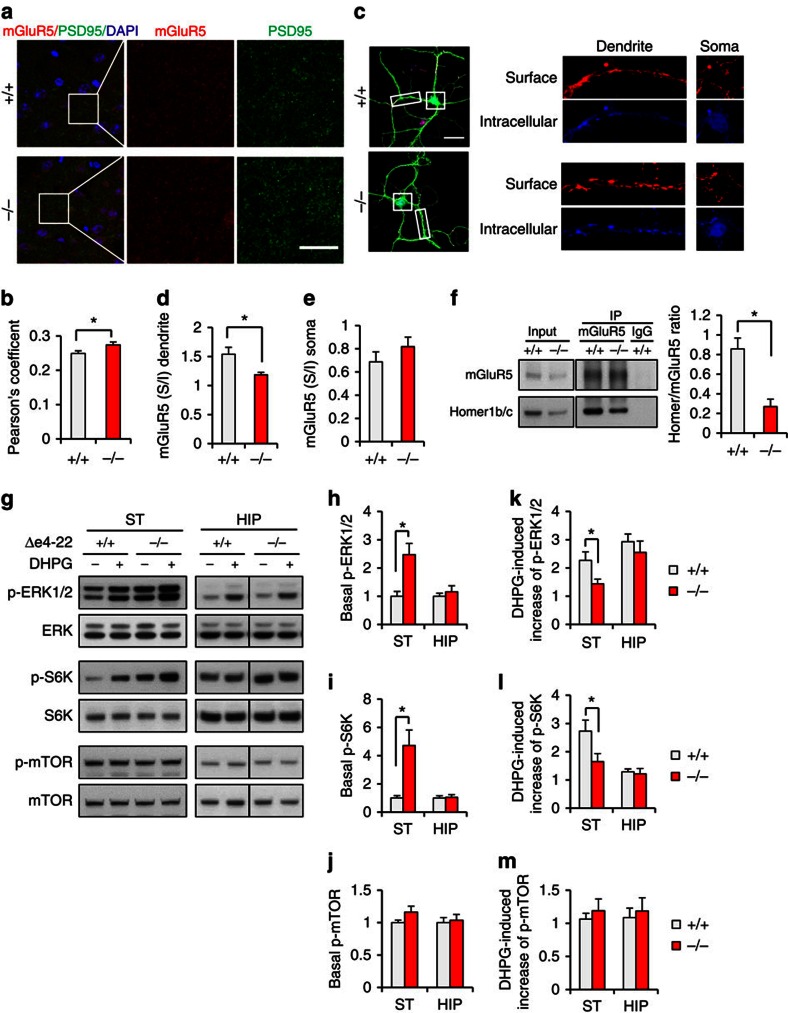
Figure 7. Abnormal accumulation of mGluR5 in PSD and altered mGluR5-Homer1 scaffolds in Δe4–22−/− striatum.
(a) Immunostaining for mGluR5 (red) and the postsynaptic marker PSD-95 (green) in −/− and +/+ striata. Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Co-localization analysis revealed a higher correlation between mGluR5 and PSD-95 in the striatum of −/− mice; *P<0.05, t-test, n=24 slices from 3 mice/genotype. (c, left) Immunostaining of surface mGluR5 (red), intracellular mGluR5 (blue), and DARPP-32 (green) in dissociated striatal MSNs. (right) Sample images of surface and intracellular mGluR5 immunostaining in dendrites and somata. (d,e) The ratio of surface/intracellular mGluR5 is decreased in dendrites (d), but is not different in somata of MSNs between genotypes; *P<0.01, t-test, n=14 cells from three mice/genotype. (f) Co-immunoprecipitation of mGluR5 and Homer1b/c revealed a decreased association in −/− striatum. *P<0.01, t-test, n=4 mice/genotype (g) Immunoblots show that basal levels of p-ERK1/2 and p-S6K are increased in −/− striatal slices. (h–j) The basal levels of p-ERK1/2 (h) and p-S6K (i), but not p-mTOR (j) were significantly increased in the striatum (ST) of −/− mice. *P<0.05, two-tailed t-test. (k–m), DHPG had a significant smaller effect on p-ERK1/2 (k) and p-S6K (l) levels in −/− ST, but the effect on p-mTOR levels (m) was similar between genotypes. The net increase of phosphorylation for each kinase was calculated by normalizing DHPG-induced phosphorylation to corresponding basal phosphorylation. *P<0.05, two tailed t-test. For ERK, n=21 for each genotype in ST, n=11 for each genotype in hippocampus (HIP). For S6K, n=16 for each genotype in ST, n=8 for each genotype in HIP. For mTOR, n=19 for each genotype in ST, n=8 for each genotype in HIP. Experiments for western blots were repeated at least three times. All data expressed as means±s.e.m.