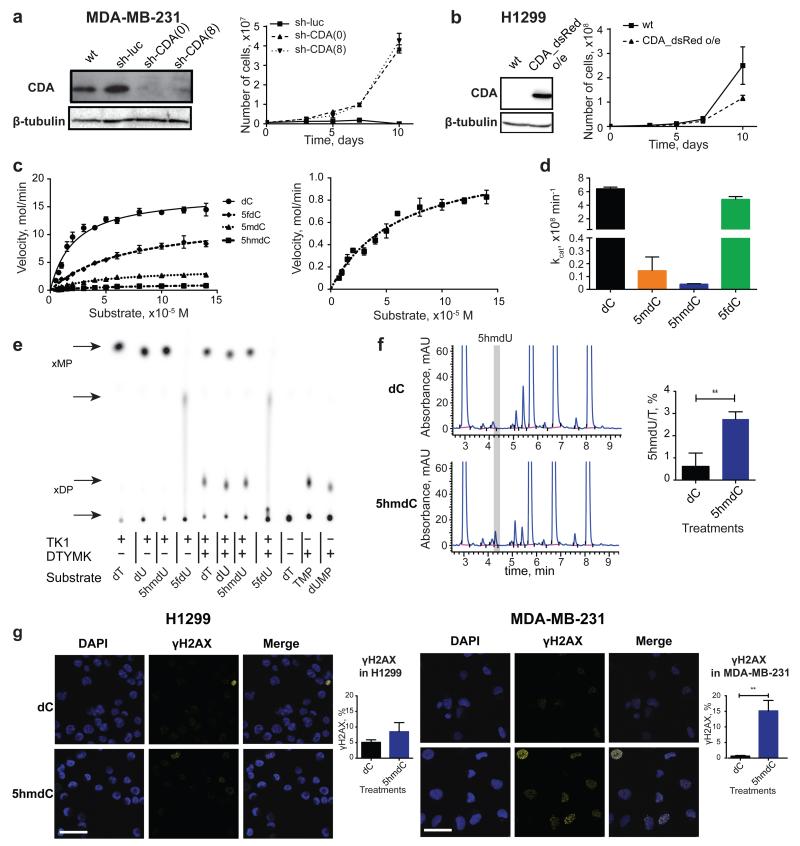
Figure 3. Molecular mechanism of CDA-dependent cytotoxicity of cytidine variants.
a, Western blot showing knock-down of CDA by sh-RNA in the MDA-MB-231 cell line. Right panel illustrates growth curves of derived stable cell lines after treatment with 10 μM 5hmdC (n=3, standard deviation is shown). (0) and (8) indicates two different sh-RNA constructs used for the experiments. b, Western blot showing overexpression of CDA after lentiviral transduction of H1299 cells with a construct overexpressing CDA (CDA_dsRed). The right panel shows the growth curve after treatment with 10 μM 5hmdC (n=3, standard deviation is shown). c, CDA activity fitted to the Michaelis-Menten model. The right panel shows a zoomed-in curve, when 5hmdC was used as a substrate. d, kcat values of CDA supplied with cytidine variants. e, TLC separation of reaction products of TK1 and DTYMK kinases, which were exposed to different modified uridine substrates. xMP indicates monophosphates and xDP indicates diphosphates. f, HPLC-UV chromatogram of nucleosides from DNA of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 10 μM 5hmdC or dC for 3 days. The right panel shows the abundance of 5hmdU relative to T (n=3, standard deviation is shown, t-test, p=0.0057). g, γH2AX immunofluorescence in MDA-MB-231 and H1299 cell lines at day 3 after treatment with 10 μM 5hmdC or dC. Scale bar = 50 μm. Below are quantifications of cells showing positive signals (n=3, standard deviation is shown, t-test, p=0.0017).