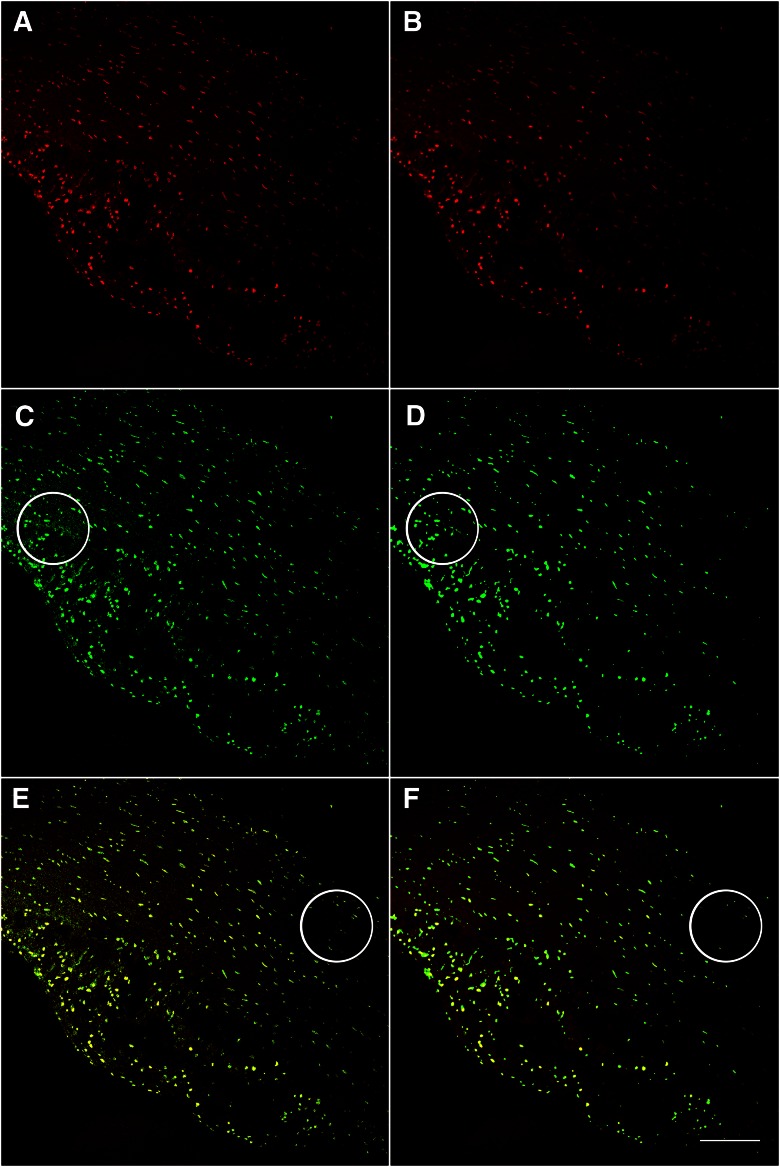
Figure 3.
Application of a median filter improves object and background segmentation. Image acquired with 20×/0.7 NA objective lens, 1024 × 1024 frame size. The raw image (A) was directly binarized using the maximum entropy FIJI/ImageJ algorithm (U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA; C) with the result overlaid onto the original image (E). Note that use of this approach resulted in background pixels interpreted as signal, indicated by a large circle in C. B) The result of a median filter applied to the original image, subsequent binarization using the maximum entropy method (D), and overlay (F). Note the improvement of signal-to-noise segmentation by removing background before binarization in D compared with C, indicated by large circles. However, both approaches failed to identify low-intensity objects, designated by circles in E and F. Original scale bar, 120 µm.