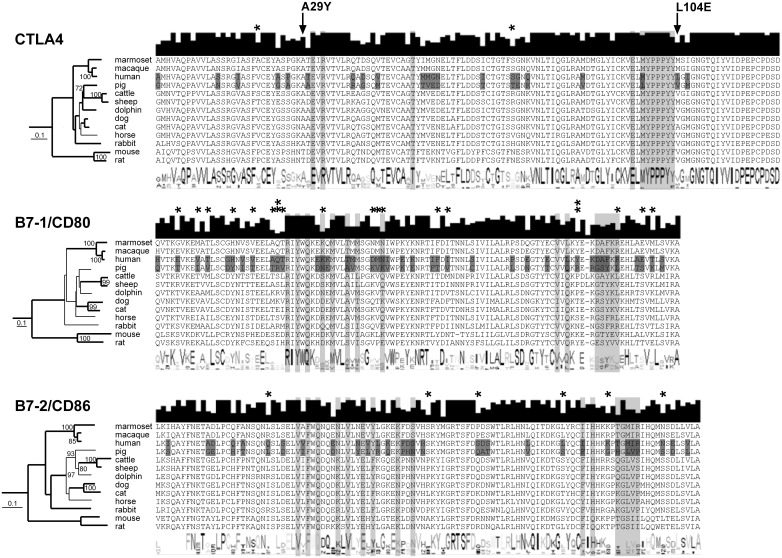
Fig 1. Binding regions in mammalian CTLA4, CD80 and CD86.
The species are arranged according to their phylogenetic pattern, with positions highlighted in light gray that were identified as essential for binding (according to [12]) and positions that differ between human and pig highlighted in dark gray. The phylogenetic trees represent genetic distance trees, with relationships also occurring in most parsimony trees shown as bold lines and bootstrap values indicating when branches occurred >70 times in the consensus of 100 genetic distance trees. For each alignment, the consensus amino acid sequence is shown below and the degree of conservation shown above the alignment. Sites of positive selection were defined by the codonML software, using the model algorithms 3 (discrete, naïve empirical bayes) and 8 (beta&omega>1, naïve empirical bayes). The sites under positive selection are marked with an asterisk, and those proposed to be under significantly (p>95%) positive selection are marked with two asterisks. The two positions that have been modified in human CTLA4 to generate LEA29Y are marked by an arrow.