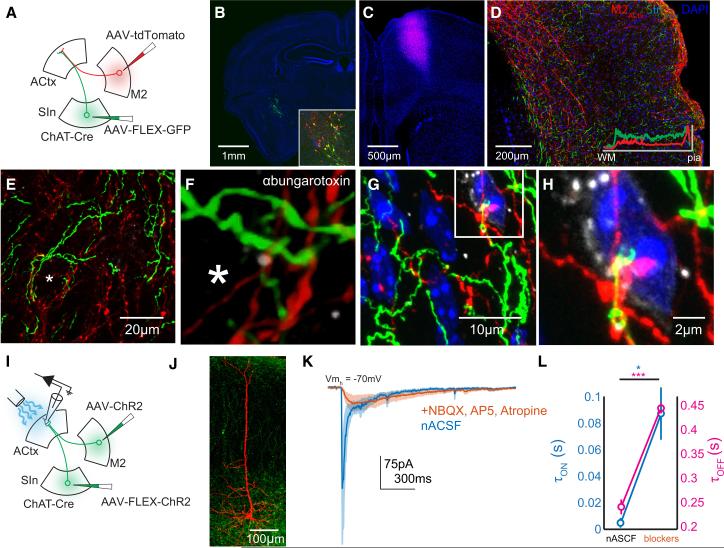
Figure 7. SInACh and M2ACtx Synapses Converge on Single Auditory Cortical Neurons.
(A) Schematic of the experimental strategy. AAV-FLEX-GFP was injected into SIn of ChAT-Cre mice. AAV-tdTomato was injected into the M2 of the same mice. (B) Confocal micrograph showing GFP labeling at the injection side. Blue is DAPI. The inset shows the injection site, immunostained for ChAT (red). (C) tdTomato labeling at the M2 injection site. (D) Labeling from SInACh (green) and M2ACtx (red) axons in ACtx. The inset shows the fluorescence intensity of SInACh and M2ACtx labeling across layers (averaged measurements from several brain sections). (E) Higher magnification Z stack showing SInACh and M2ACtx axons near a putative cell body (asterisk). (F) Higher magnification image from (E). The Z stack was interpolated and rotated slightly. Nicotinic ACh receptors are labeled with ɑ-bungarotoxin (greyscale). (G) Another Z stack showing SInACh and M2ACtx axons near a cell body from a different mouse. DNA is labeled with DAPI. (H) Higher magnification Z stack from (G). (I) Schematic of the experimental strategy. AAV-FLEX-ChR2-GFP was injected into SIn of ChAT-Cre mice. AAVChR2-GFP was injected into the M2 of the same mice. Whole-cell voltage clamp recordings were made from acute coronal ACtx brain slices. (J) Confocal Z stack showing a pyramidal neuron labeled following whole-cell recording surrounded by ChR2-expressing axons. (K) Average traces of excitatory currents (5 neurons) in response to photostimulation of putative SInACh and M2ACtx axons in normal ACSF (blue) and following application of blockers (orange; the shading indicates SEM). Nicotinic transmission is preserved after blocking glutamatergic M2ACtx currents. (L) Onset (blue) and offset (magenta) time constants of excitatory currents from (J).