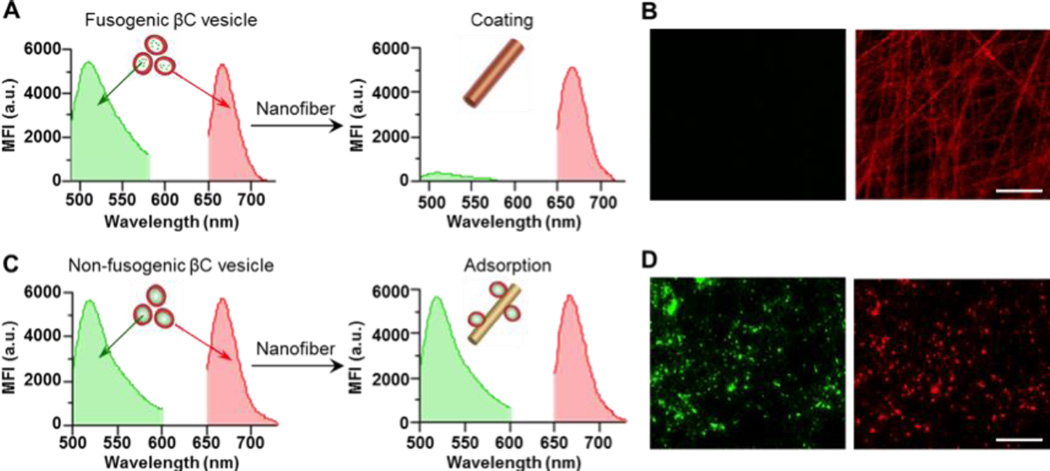
Fig. 2.
Confirming the fusion of the βC vesicles onto the nanofibers. (A,B) The βC vesicles were labeled with two distinct fluorescent dyes: DiD (red) in the cell membrane and calcein-AM (green) in the aqueous compartment of the vesicles. (A) Fluorescence emission spectra of the βC vesicles (left panel) and CM-fibers (right panel). (B) Fluorescent images of the CM-fibers in the green channel (left panel) and the red channel (right panel). (C,D) The βC vesicles (labeled with DiD, red) were pre-coated onto PLGA polymeric nanoparticles (labeled with Alexa 488, green) to passivate their fusion ability. (C) Fluorescence emission spectra of the non-fusogenic βC vesicles (left panel) and their mixture with the nanofibers (right panel). (D) Fluorescent images of the nanofibers after incubation with the non-fusogenic βC vesicles in the green channel (left panel) and the red channel (right panel). Scale bars, 25 µm.