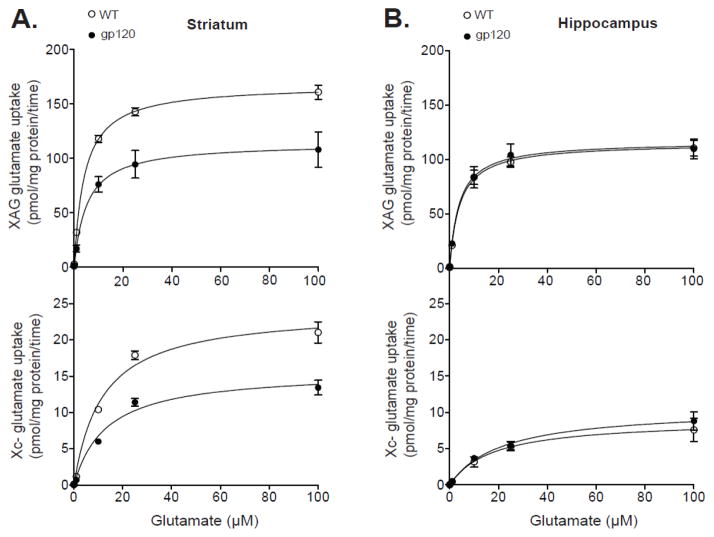
Figure 1.
System XAG and xc- glutamate uptake in crude (mixed) synaptosomes from striatum and hippocampus of gp120 and wild-type (WT) mice. The maximal velocity of XAG (i.e., sodium-dependent) and xc- (i.e., sodium-independent) glutamate uptake (pmol/mg protein/time) was plotted as a function of the external unlabeled glutamate concentration. Saturation analysis was performed using 100 nM of L-[3H]-glutamate in the absence or presence of unlabeled L-glutamate (0-100 μM) to give the final concentrations shown (x-axis). The maximal velocity (Vmax) and the affinity (Km) constants were determined by nonlinear regression analysis by applying the Michaelis Menten Equation to the data. Significant differences in the estimated Vmax and Km values were determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA). A significant (p<0.05) reduction in the Vmax of both systems XAG and xc- glutamate uptake was observed in striatum (A) but not hippocampus (B) of gp120 mice compared to WT. There were no significant group differences in the Km (affinity) for glutamate in either glutamate uptake systems in striatum and hippocampus. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4/group).