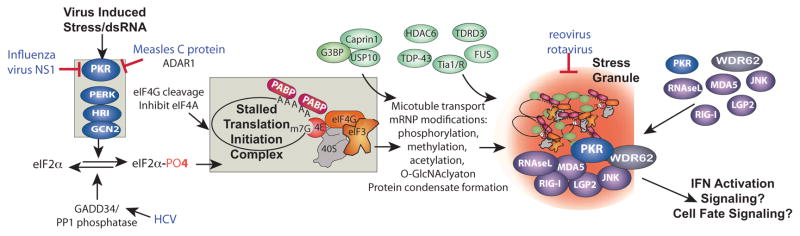
Figure 1.
PKR dependent stress granule assembly pathway, innate immune factors that enter stress granules and interference by RNA virus modulation of PKR. Virus infection causes stress at multiple levels by restricting translation through activation of eIF2 kinases, principally PKR, or by causing cleavage or inactivation of other translation initiation factors. These translation insults convert active polysome mRNPs into stalled translation initiation complex mRNPs containing 40S ribosome subunits, initiation factors and mRNAs (boxed). A complex series of events involving nucleation of multiple stress granule proteins such as G3BP1, Tia-1/TIAR, TDRD3, FUS, TDP43 and HDAC6 plus transport of mRNP complexes on microtubules leads to aggregates of translation initiation complex mRNPs in stress granules. Reovirus and rotavirus can repress SGs, but mechanisms are not known, points of interaction of other viruses with this scheme are indicated. Note that many viruses control PKR activation; only those discussed in the text are indicated.