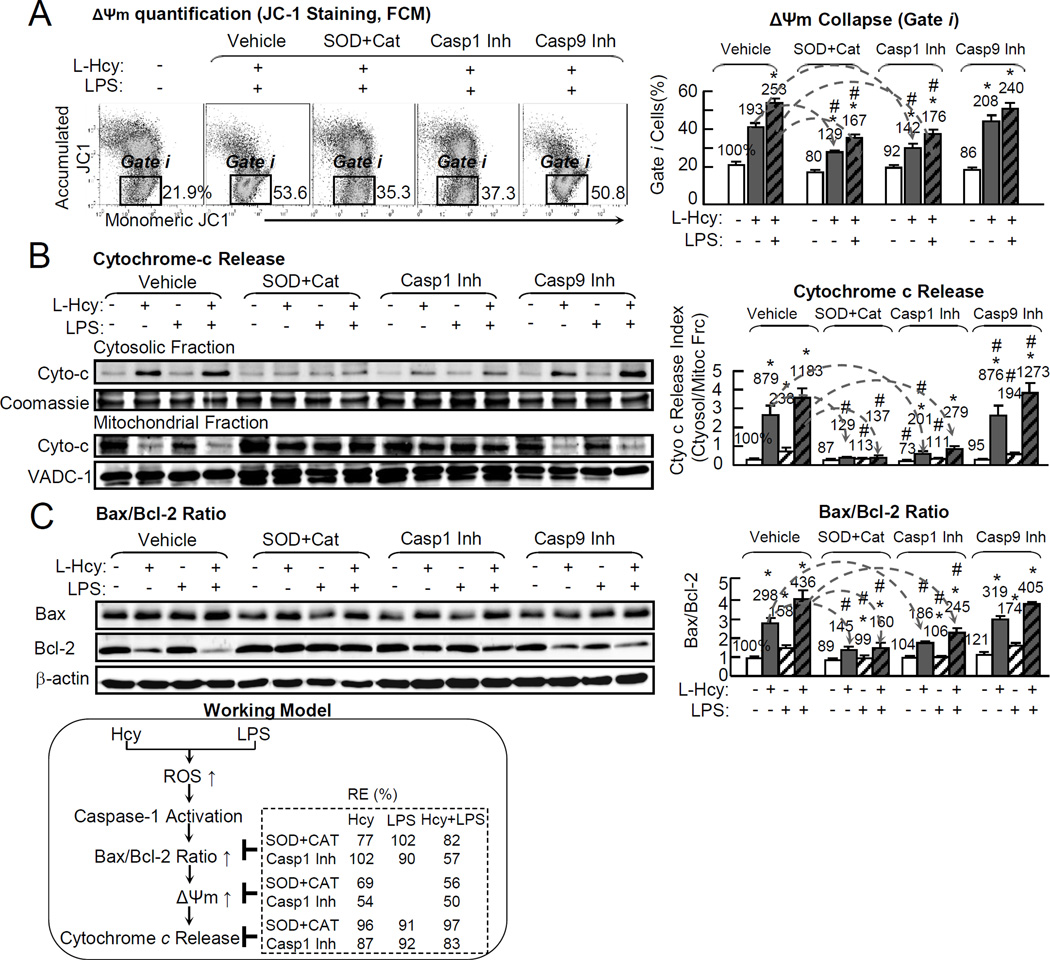
Figure 7. Hcy induces Δψm collapse and cytochrome-c release, and increase Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio via oxidative stress, Casp1 activation in ECs.
HUVECs were cultured in 6cm dish and treated with L-Hcy (500µM) and/or LPS (10 µg/mL) as described in Fig. 1. Cells were pretreated with antioxidants-adenoviral ec-SOD (1MOI) (WB shown in online Figure IX) for 48hr and PEG-catalase (25mg/mL) for 30min, or Casp1, 9 inhibitors for 30min, prior to Hcy/LPS treatment. Mitochondrial function was accessed by JC-1 staining to determine Δψm. Apoptosis signaling was examined by WB for Bax (pro-apoptotic protein) to Bcl-2(anti-apoptotic) ratio. A, Δψm quantification (JC-1 staining, FCM). Δψm collapse cells were quantitated as percentage in gate i. Δψm detection by JC-I staining by fluorescent microscope images shown in online Figure X. B, Cytochrome-c (WB). Cell homogenates were separated to cytosolic and mitochondrial fraction for cytochrome-c protein content by WB. Cytochrome-c ratio (cytosolic fraction/mitochondrial fraction content) was calculated to reflect its leakage from mitochondrial to cytosol. Coomassie blue staining and VADC-1 (mitochondrial protein) were used as loading controls. C, Bax/Bcl-2 (WB). Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was examined by WB. Bax/Bcl-2 ratio is used as apoptosis/pyroptosis index. Arrows indicate the direction of significant changes. Values are Mean±SEM; n=4. Numbers above each bar is the percentage normalized by the mean of control. *, P<0.05 vs control in same group; #, P<0.05 vs same treatment in vehicle. Δψm, mitochondrial potential.