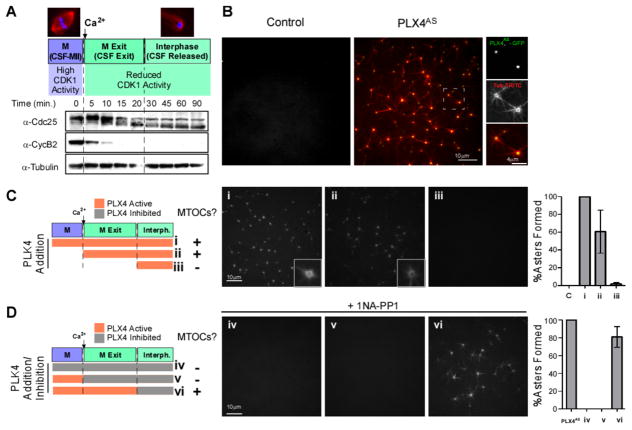
Figure 1. PLX4 induces de novo aster formation early after M-phase (CSF) release in Xenopus egg extracts.
A. Cell cycle profiling of Xenopus M-phase extracts released with Ca2+. Western blots (WB) show the kinetics of Cdc25 downshift and CyclinB2 degradation leading to reduced CDK1 activity. B. GFP-PLX4AS-induces MTOC formation in M-phase released extracts. CSF extract was incubated with 0.65 μM GFP-PLX4AS, (green) and TRITC-tubulin (red). See also Figure S1, S2C for the generation and characterization of Shokat alleles. (See also Movie S1 and S2) C. Cell cycle-dependent effect of PLX4. rPLX4 was added at different time points: (i) 10 mins before release (add Ca2+), (ii) concomitantly with release, and (iii) 20 mins after release, in order to check when PLK4 activity is needed to form MTOCs (TRITC-tubulin). D. Inhibition of PLX4AS using 1 NA-PP1 at different stages. PLX4AS was added 10 mins before Ca2+ and was inhibited by 1NA-PP1 in extracts at different time points: (iv) at time zero (v) with Ca2+, and (vi) 20 mins after Ca2+. Panels of MTOCs formed in the extract under each condition, stained with TRITC-tubulin, are shown. Asters were counted in 10 images for each condition, and normalized to the number of asters observed in control extracts ((i) in C and PLX4AS in D) (n=3, Bars represent average +/−SD).