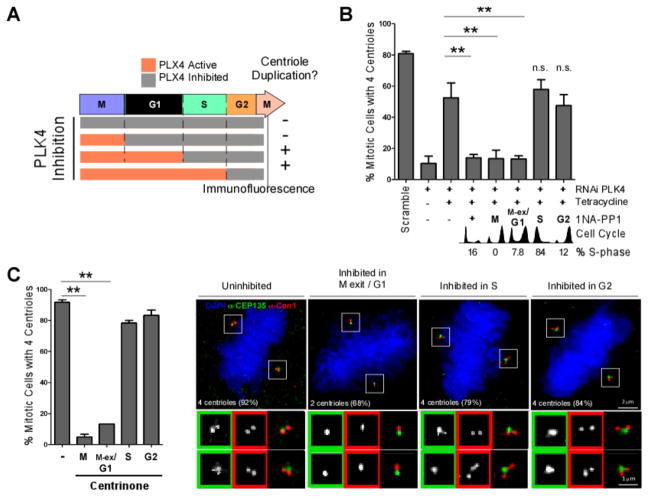
Figure 2. PLK4 activity is needed at M-phase exit/G1 for centriole duplication in human cells.
A–C. PLK4 activity was inhibited at different cell cycle times by 1NA-PP1 (PLK4AS) (B) or centrinone (C), and centrioles were counted in the subsequent mitosis. A. Experimental scheme and summary of results from B–C. B. 1NA-PP1 was added to cells expressing PLK4AS and depleted of endogenous PLK4 at 0 hrs (positive control, (+)), 6 (G2), 8 (M), 10 (M-exit/G1) and 20 hrs (S-phase) following S-phase block release. Cells were fixed in the immediate subsequent mitosis, and centrioles counted (n=3, 100 cells/condition, mean +/− SEM. ** = p<0.01). Cell cycle profiles were obtained by flow cytometry. Percentage of S-phase cells at time of inhibition were monitored by EdU staining (See also Figure S2F–I for controls). C. Centrinone was added at the indicated cell cycle stages and centrioles were counted in the subsequent mitosis. (n=3, 100 cells/condition. mean +/− SEM. ** = p<0.01). Representative immunofluorescence images of mitotic cells stained as indicated, following inhibition of PLK4 by centrinone. The number of centrioles found with the highest frequency upon inhibition is shown (average of 3 experiments). See Figure S2J for detailed quantitation.