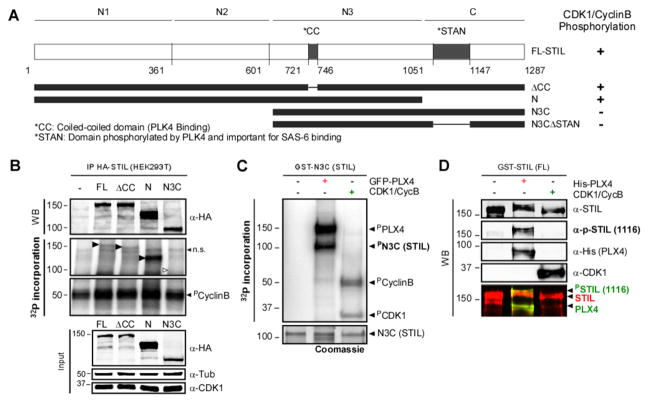
Figure 5. CDK1/CyclinB phosphorylates STIL outside of the PLK4 interacting domain in human cells.
A. Schematic representation of HA- and GST-tagged STIL constructs. The evolutionary conserved coiled-coil (CC; PLK4-binding) and STAN (PLK4-phosphorylated and SAS6 binding) domains are indicated. Constructs were used for phosphorylation assays. The results are summarized on the right. B. CDK1/ Cyclin B can phosphorylate STIL on its N-terminus. Autoradiography of an In vitro kinase assay using IP control, or HA-STIL (FL, ΔCC, N and N3C), CDK1/Cyclin B and ([γ-32P]-ATP). Black arrows show phosphorylated fragments. White arrow indicates the expected position of the non-phosphorylated N3C fragment (n.s.=non-specific). Note that all fragments, but not the N3C, are phosphorylated by CDK1/CyclinB. C. STIL-N3C, the domain that interacts with PLK4 and SAS6, is not phosphorylated by CDK1/CyclinB. Incorporation of [γ-32P] on STIL-N3C incubated with GFP-PLX4 or CDK1/CyclinB was visualized by autoradiography. D. CDK1/CyclinB does not phosphorylate STIL on the site phosphorylated by PLK4 (S1116). Recombinant GST-STIL (FL) was incubated with rPLX4 or CDK1/CyclinB. Samples were analyzed by WB using anti-pS1116-STIL (which recognizes a PLK4-specific phosphorylation [8]), anti-His and anti-CDK1 to monitor loaded proteins.