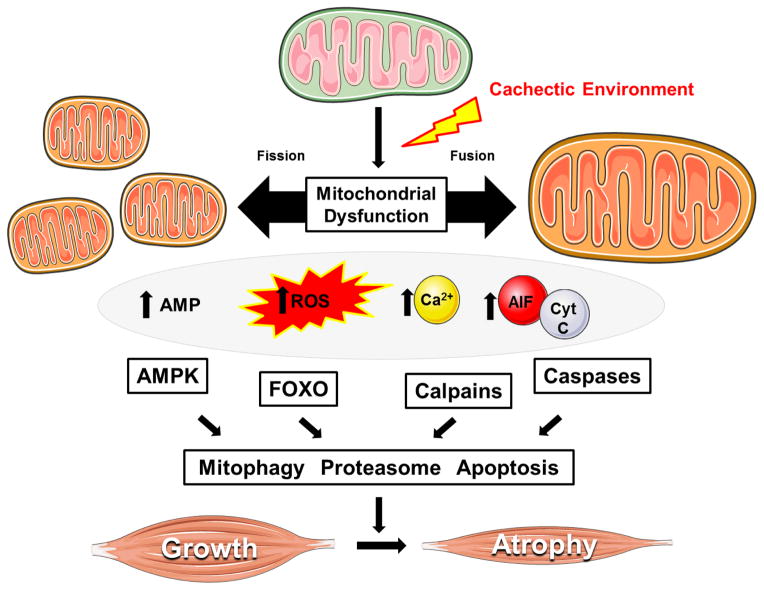
Figure 2. Mechanisms related to skeletal muscle mitochondria dysfunction that can regulate cancer-induced wasting.
The progression of cancer cachexia is associated the disruption of mitochondrial quality (i.e. biogenesis, dynamics, mitophagy), which can lead to the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria. Impaired mitochondrial function promotes energetic stress, ROS production, and the cytoplasmic localization of calcium and pro-apoptotic factors. Several key catabolic signaling pathways are activated leading to skeletal muscle atrophy, as well as further impairments in muscle oxidative metabolism. Abbreviations: Adenosine monophospate (AMP). 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Apoptosis-inducing Factor (AIF). Cytochrome C (Cyt C). Forkhead Box O (FOXO). Figure was made with Servier Medical Art (http://www.servier.com/Powerpoint-image-bank).