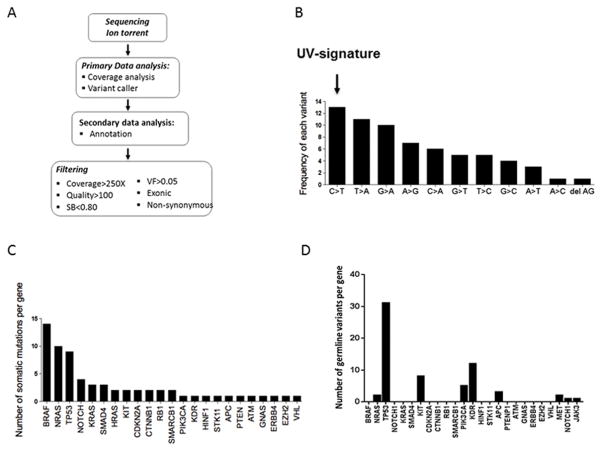
Figure 1.
Ion Torrent analysis of the pilot melanoma cohort (n=34) and identification of somatic and germline mutations in melanoma. A) Ion Torrent sequencing analysis workflow. The AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2 assay was used to amplify DNA from tumor and matched germline controls from melanoma patients. Sequencing data underwent a primary analysis using the Torrent Suite server. Secondary analysis (annotation) was performed by uploading VCF files into Ion Reporter using the ion reporter uploader plugin. B) A UV-induced signature is the most frequent somatic variation identified in our cohort. C) The frequencies of somatic mutations identified in BRAF, NRAS and KIT genes in our cohort are consistent with previously reported distributions in melanoma. D) Ion Torrent sequencing identified 9 germline variants in our pilot melanoma patient cohort (NRAS, TP53, KIT, PIK3A, KDR, APC, MET, NOTCH1, JAK3).