Fig. 1.
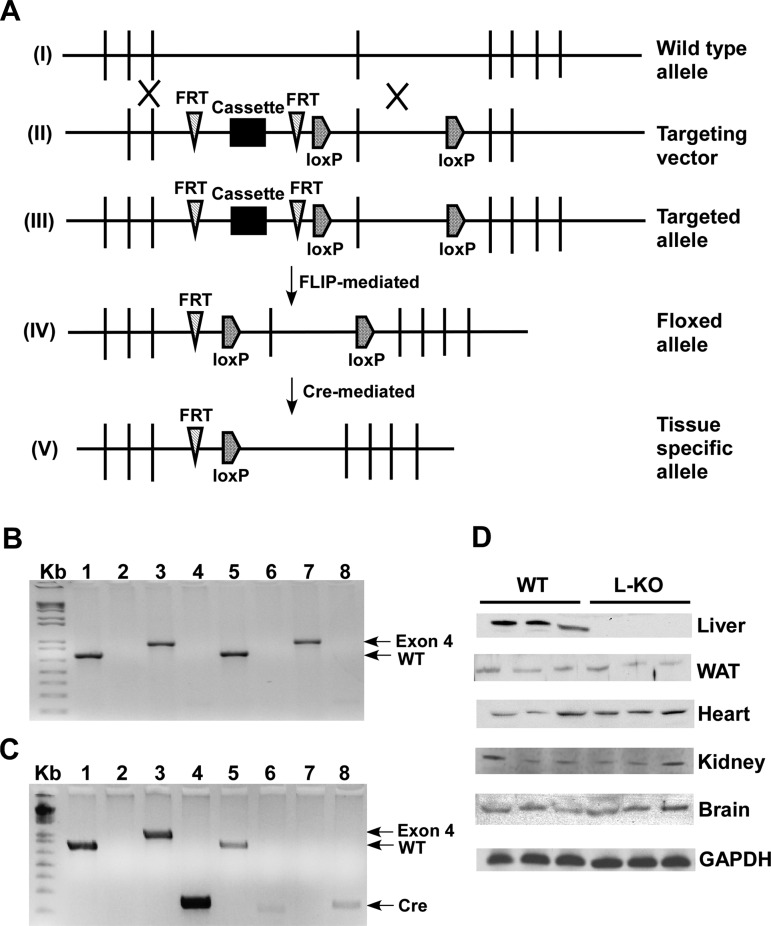
Conditional targeting of the Perilipin 2 (Plin2) allele allows for liver-specific deletion. A: targeting strategy of generating Plin2 liver-specific knockout (L-KO) mice. I: wild-type (WT) allele. II: targeting vector. III: targeted allele. IV: floxed allele. V: tissue-specific allele. B: PCR screening of WT mice. Primers were designed to detect the presence or absence of the WT allele (lane 1, 850 bp), FRT site (lane 2, 204 bp), exon 4 (lane 3, 1 Kb), and the Cre gene (lane 4, 233 bp) in tail (lanes 1–4) and liver (lanes 5–8) samples. Mice containing the floxed allele are positive for the WT gene (lane 1) and exon 4 (lane 3) but lack bands corresponding to the FRT site (lane 2) and Cre gene (lane 4). C: PCR screening of L-KO mice. Tail DNA (lanes 1–4) from L-KO mice shows bands corresponding to the WT gene (lane 1), exon 4 (lane 3), and the Cre gene (lane 4). L-KO liver DNA (lanes 5–8) is positive for the WT gene (lane 5) and the Cre gene (lane 8), but exon 4 is not detected (lane 7), indicating tissue-specific deletion. D: Western blot analysis of Plin2 protein expression in liver, white adipose tissue (WAT), heart, kidney, and brain using GAPDH as a loading control.