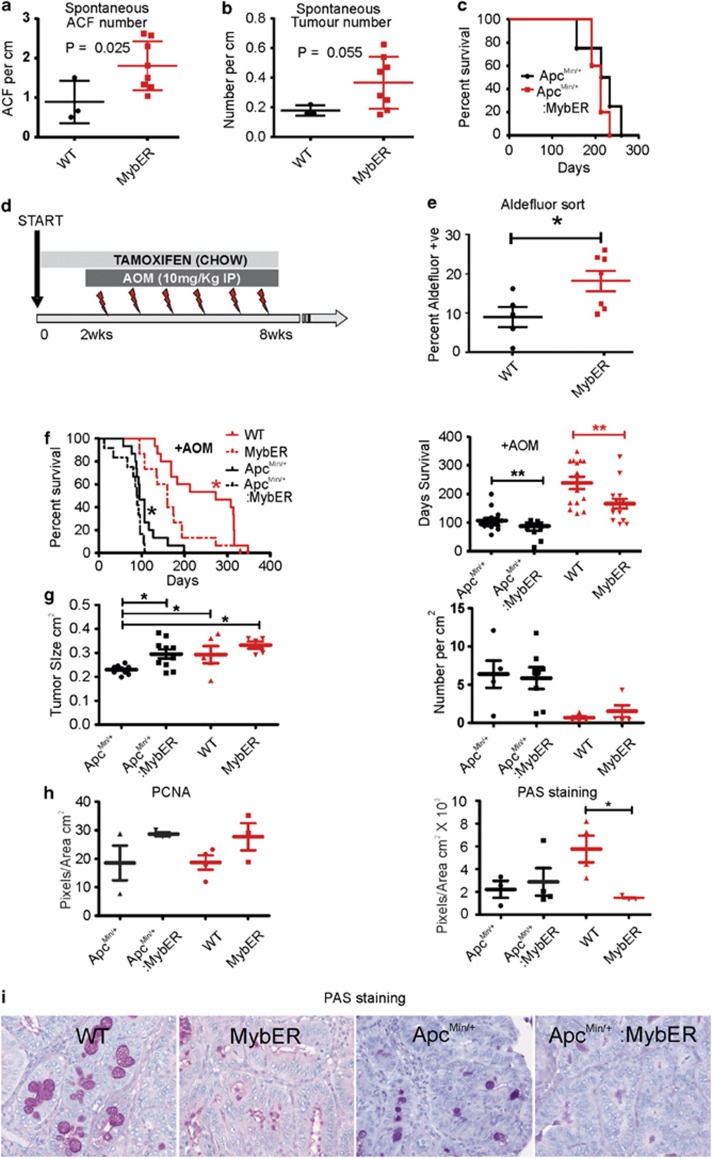
Figure 3.
MybER-activation accelerates CRC initiation and progression of AOM-driven CRC. (a) ACF in tamoxifen-treated MybER mice compared with WT mice on Tamoxifen at 7 months (n=3). (b) Tumor number is slightly increased in MybER mice (n=8). (c) Activation of MybER in mice on an Apcmin/+ background does not influence survival. (d) Diagram depicting the pre-treatment and continual access to tamoxifen in chow (8 weeks) and 2 weeks later the initiation of weekly AOM injections used to test the effect of Myb-induction in the initiation phase of CRC. (e) Pre-treatment by tamoxifen increases the percentage of cells with high aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identified by FACS (n>5). (f) Survival experiments were conducted to determine whether MybER-activation on a WT or Apcmin/+ (n>10) background translates into poorer survival outcome owing to AOM-induced CRC. Individual mice were harvested when they reached ethical end points defined by either bleeding from the anus, anaemia (pale feet), hunching, severe diarrhea, prolapsed anus or body weight loss >20%. Survival analysis revealed that MybER-activation on a WT and Apcmin/+ backgrounds significantly accelerated the initiation and progression of disease and reduced the life expectancy of mice after treatment. (g) Tumors generated on an Apcmin/+ background in presence of MybER were significantly larger compared with tumors arising in Apcmin/+ mice and MybER-activation did not alter the number of tumors. (h) Tumors derived from all groups were sectioned and analyzed by IHC for PCNA to assess cell proliferation and for goblet cell differentiation (i–j) using periodic acid staining (PAS). Data presented for individual samples with means ±s.e.m.; *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Survival curves were analyzed using log-rank (Mantel–Cox) Test.