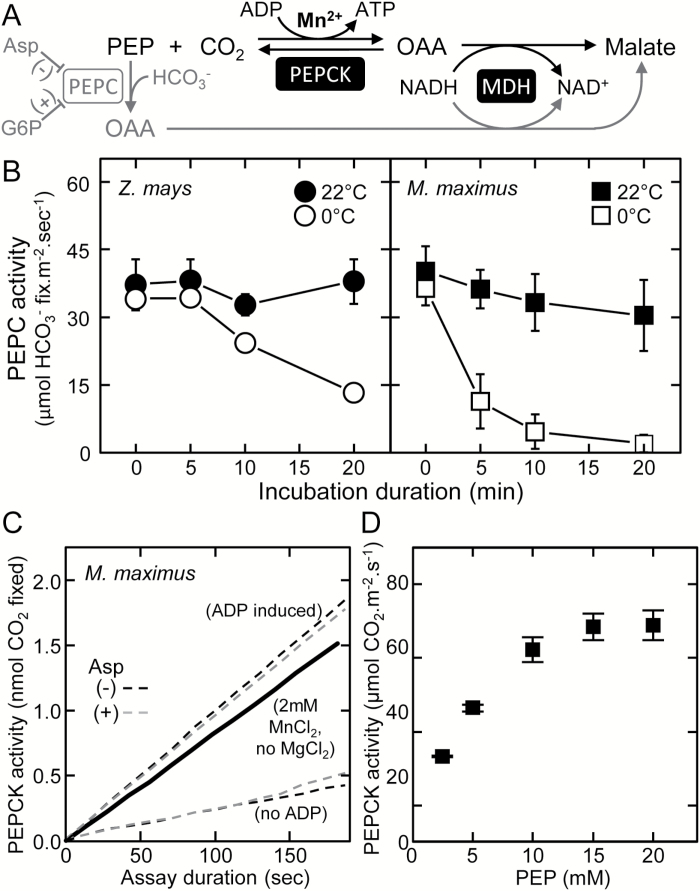
Fig. 2.
Optimizing the measurement of PEPC and PEPCK activities in leaf extract. (A) Summarizing the commonality of the malate dehydrogenase- (MDH) coupled, NADH oxidation-linked assay to quantify the carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) into oxaloacetate (OAA) by PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK; in black) and PEP carboxylase (PEPC; in gray), an enzyme inhibited (–) by aspartate (Asp; Huber and Edwards, 1975) and activated (+) by glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). (B) Effect of storage temperature (room temperature, 22 °C, or ice, 0 °C) and time on PEPC activity in the soluble protein from young leaves from mature Z. mays and M. maximus plants (n=3 biological replicates ±SD; see leaves m3b and c3b in Fig. 5A for examples). (C) Representative assay of PEP carboxylation by PEPCK measured in leaf soluble protein extract using the no MgCl2 method of Sharwood et al. (2014) ( black line) and the modified ADP method of this study in assays with (gray dashed lines) or without (black dashed lines) 5mM aspartate (a PEPC inhibitor, A). (D) Response of PEPCK activity to [PEP] in M. maximus leaf soluble protein. To prevent PEPC interference ensure: 1) No MgCl2 in assay and extraction buffers, 2) MnCl2 up to 5mM in extraction and assay buffers, 3) pH of extraction and assay buffers <7.0, 4) No glucose-6-phosphate, and 5) include aspartate in assay buffer.